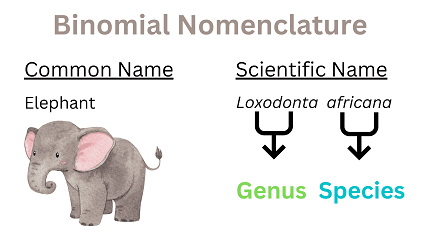
Nomenclature is the system of naming things, such as organisms, chemicals, or structures, in a specific field or discipline. It is an important aspect of communication and allows for clear and consistent identification of entities within a particular area of study. For example, in biology, the binomial nomenclature system is used to name species, with each species having a unique two-part name consisting of a genus and a specific epithet. Similarly, in chemistry, the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) provides a set of rules for naming chemicals based on their composition and structure. In general, nomenclature provides a standardized way of referring to things, which can help avoid confusion and promote clarity in communication.
What is Required Nomenclature
Required nomenclature refers to the specific naming conventions or rules that must be followed within a particular field or discipline. These conventions ensure clear and consistent communication and avoid confusion among researchers or practitioners in the field. The requirements for nomenclature can vary depending on the area of study, but they are typically established by professional organizations or governing bodies within the field.
For example, in biology, the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants provides a set of rules and guidelines for naming organisms in these groups. Similarly, in chemistry, the IUPAC provides a set of rules for naming chemicals and compounds.
Following required nomenclature is important for several reasons. It helps to avoid confusion and misinterpretation of data or findings, ensures consistency in communication and allows for easy identification and classification of entities within a particular field. Additionally, adherence to required nomenclature allows researchers and practitioners to build on each other’s work and collaborate effectively, which ultimately advances knowledge and understanding in the field.
Who is Required Nomenclature
“Required Nomenclature” is not a person or entity, but rather a term used to describe the specific naming conventions or rules that are required within a particular field or discipline. These conventions are typically established by professional organizations or governing bodies within the field, and they ensure clear and consistent communication among researchers, practitioners, and other stakeholders.
For example, in biology, the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN) and the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN) provide guidelines and rules for naming organisms in these groups. In chemistry, the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) provides rules for naming chemicals and compounds. Similarly, other fields such as geology, physics, and engineering have their own conventions for naming and classifying entities within their respective domains.
Adherence to required nomenclature is important in promoting clarity and consistency in communication, avoiding confusion and misinterpretation of data, and allowing for easy identification and classification of entities within a particular field.
When is Required Nomenclature
“Required nomenclature” is always in effect within a particular field or discipline, and the naming conventions or rules must be followed whenever referring to entities within that field. The requirements for nomenclature are typically established by professional organizations or governing bodies within the field and are intended to ensure clear and consistent communication among researchers, practitioners, and other stakeholders.
For example, in biology, the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN) and the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN) provide guidelines and rules for naming organisms in these groups. In chemistry, the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) provides rules for naming chemicals and compounds. Similarly, other fields such as geology, physics, and engineering have their own conventions for naming and classifying entities within their respective domains.
Researchers and practitioners within a particular field are expected to follow the required nomenclature whenever referring to entities within that field. Adherence to these naming conventions is important in promoting clarity and consistency in communication, avoiding confusion and misinterpretation of data, and allowing for easy identification and classification of entities within a particular field.
How is Required Nomenclature
“Required nomenclature” is the set of specific naming conventions or rules that must be followed within a particular field or discipline. The guidelines and rules for nomenclature are typically established by professional organizations or governing bodies within the field, and they ensure clear and consistent communication among researchers, practitioners, and other stakeholders.
How to use required nomenclature varies depending on the field or discipline. In biology, for example, the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN) provides rules and guidelines for naming organisms in these groups, while the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN) provides similar guidelines for animals. In chemistry, the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) provides rules for naming chemicals and compounds.
To use required nomenclature, researchers and practitioners within a field must be familiar with the established guidelines and rules and follow them whenever referring to entities within that field. This can involve using specific prefixes or suffixes, using standardized abbreviations, or following specific naming conventions, among other things. Adherence to required nomenclature is important in promoting clarity and consistency in communication, avoiding confusion and misinterpretation of data, and allowing for easy identification and classification of entities within a particular field.
Production of Nomenclature
The production of nomenclature typically involves the establishment of guidelines and rules for naming entities within a particular field or discipline. These guidelines and rules are typically developed by professional organizations or governing bodies within the field, often through a consensus-based process involving experts and stakeholders.
The process of developing nomenclature can involve extensive research, consultation, and revision to ensure that the guidelines and rules are clear, accurate, and widely accepted within the field. This can involve reviewing existing nomenclature, considering new discoveries or developments within the field, and addressing any ambiguities or inconsistencies in current practices.
Once the guidelines and rules for nomenclature are established, they are typically published in a form that is accessible to researchers, practitioners, and other stakeholders within the field. This may involve the creation of an online resource, a printed publication, or both.
Researchers and practitioners within a field are expected to be familiar with the established guidelines and rules for nomenclature and to follow them whenever referring to entities within that field. Adherence to these guidelines and rules is important in promoting clarity and consistency in communication, avoiding confusion and misinterpretation of data, and allowing for easy identification and classification of entities within a particular field.
Case Study on Nomenclature
One example of the importance of nomenclature is the case of the Zika virus outbreak in 2015-2016. The Zika virus is a flavivirus that is primarily transmitted by Aedes mosquitoes and was first discovered in Uganda in 1947. However, the virus was not widely known or studied until the outbreak in Brazil in 2015-2016, which resulted in a global health emergency.
During the outbreak, there was confusion and inconsistencies in the nomenclature used to refer to the virus, which caused confusion and hindered communication among researchers, practitioners, and policymakers. The virus was known by several names, including Zika virus, Zika fever, and Zika virus disease, among others.
To address this issue, the World Health Organization (WHO) established a temporary nomenclature for the virus, which included referring to it as “Zika virus” and using the abbreviation “ZIKV” in scientific literature. This nomenclature was widely adopted by researchers, practitioners, and policymakers, and helped to promote clarity and consistency in communication about the virus.
However, the temporary nomenclature was not without controversy. Some experts argued that it was too simplistic and did not reflect the complexity of the virus, which has several different strains and can cause a range of symptoms. Others argued that the temporary nomenclature should have included a designation for the outbreak in Brazil, which was distinct from other strains of the virus.
Despite these criticisms, the temporary nomenclature established by WHO was successful in promoting clear and consistent communication about the Zika virus during the outbreak. The episode highlights the importance of nomenclature in promoting effective communication and collaboration within a field, particularly in the context of a rapidly evolving public health crisis.
White paper on Nomenclature
Introduction:
Nomenclature is the system of rules and conventions for naming entities within a particular field or discipline. It is important for promoting clarity and consistency in communication, avoiding confusion and misinterpretation of data, and allowing for easy identification and classification of entities within a particular field. This white paper explores the significance and relevance of nomenclature in various fields and discusses the challenges and opportunities associated with its use.
Importance of Nomenclature:
Nomenclature is essential for effective communication within a field. Without a standardized system for naming entities, confusion and misinterpretation of data can occur, hindering progress and collaboration. In fields such as biology, chemistry, and medicine, where precise identification and classification of entities is critical, adherence to nomenclature is particularly important.
Nomenclature also plays a critical role in promoting the reproducibility of research. Clear and consistent naming conventions allow for the easy identification and replication of experiments and results, facilitating the advancement of knowledge in a field.
Challenges in Nomenclature:
Despite its importance, nomenclature can be challenging to establish and maintain. The process of developing and revising nomenclature can be time-consuming and contentious, requiring consensus-based decision-making among experts and stakeholders within a field.
Additionally, nomenclature can be subject to changes over time as new discoveries and developments occur within a field. This can lead to confusion and inconsistencies in naming conventions, requiring ongoing efforts to update and revise nomenclature to reflect current understanding and best practices.
Opportunities for Improving Nomenclature:
Advances in technology and data science are providing new opportunities for improving nomenclature in various fields. For example, machine learning algorithms can be trained to automatically classify and name entities based on their characteristics, potentially reducing the need for human input and subjectivity in the naming process.
In addition, efforts are underway to promote the standardization and harmonization of nomenclature across different fields and disciplines. For example, the FAIR (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, Reusable) principles for data management and sharing emphasize the importance of standardized naming conventions to promote the interoperability and reuse of data across different fields.
Conclusion:
Nomenclature is a critical component of effective communication and collaboration within a field. Despite the challenges associated with its establishment and maintenance, ongoing efforts to improve and standardize nomenclature are essential for promoting the reproducibility and advancement of knowledge in various fields. As technology and data science continue to evolve, there are opportunities for new approaches and tools to further enhance the use and effectiveness of nomenclature.