Lenz Law
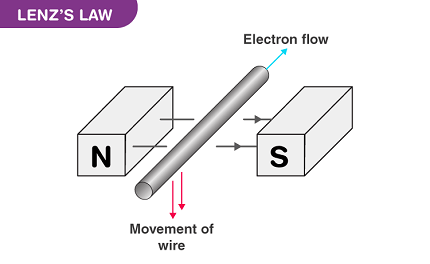
Lenz’s Law is a fundamental principle in electromagnetism that describes the direction of an induced current in a conductor when it is exposed to a changing magnetic field. It states that the induced current in a conductor will flow in a direction that opposes the change in magnetic flux that caused it.
When a magnetic field through a conductor increases or decreases, an induced current will flow in the conductor in such a way that it creates a magnetic field that opposes the change. This phenomenon is commonly observed in electromagnetic induction, electric generators, and transformers.
Lenz’s Law can be summarized as follows:
- When the magnetic field through a conductor increases, the induced current will flow in such a way that it produces a magnetic field opposing the increase.
- When the magnetic field through a conductor decreases, the induced current will flow in such a way that it produces a magnetic field opposing the decrease.
Lenz’s Law is essential in understanding the behavior of induced currents and plays a crucial role in various practical applications, including electric power generation, transformers, and electromagnetic braking systems. It helps ensure that energy is conserved and provides a basis for understanding the interactions between magnetic fields and conductors.
The syllabus for the Advanced Course AIIMS in Physics includes Lenz’s Law. Lenz’s Law is a fundamental principle in electromagnetism that describes the direction of an induced current in a conductor when it is exposed to a changing magnetic field.
Lenz’s Law states that the induced current in a conductor will always flow in a direction that opposes the change in magnetic flux that caused it. This means that when a magnetic field through a conductor increases or decreases, an induced current will flow in the conductor in such a way that it creates a magnetic field that opposes the change.
In terms of syllabus content, you should focus on understanding the concept of Lenz’s Law, its applications, and the factors that determine the magnitude and direction of the induced current. Additionally, you should also learn about the use of Lenz’s Law in various practical applications, such as electromagnetic induction, electric generators, and eddy currents.
It’s important to note that while I can provide a general overview of the topic, the specific details and depth of coverage may vary depending on the course and curriculum. I recommend referring to the official course materials or consulting with your instructor for a more detailed syllabus and study materials tailored to your specific needs.
What is Required Physics syllabus Lenz Law
The required physics syllabus for studying Lenz’s Law typically includes the following topics:
- Magnetic Flux: Understanding the concept of magnetic flux, its calculation, and its relationship with the magnetic field and area.
- Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction: Familiarity with Faraday’s law, which states that a changing magnetic field induces an electromotive force (emf) in a conductor.
- Lenz’s Law: Understanding the statement and implications of Lenz’s Law, which states that the induced current in a conductor will flow in a direction that opposes the change in magnetic flux.
- Induced Electromotive Force (emf): Exploring how the changing magnetic field leads to the creation of an induced emf in a conductor and its relationship with the rate of change of magnetic flux.
- Direction of Induced Current: Determining the direction of the induced current based on Lenz’s Law and the direction of the changing magnetic field.
- Applications of Lenz’s Law: Examining practical applications of Lenz’s Law, including electric generators, transformers, eddy currents, electromagnetic braking, and electromagnetic induction experiments.
It’s important to note that the depth of coverage and specific details may vary depending on the educational institution and the level of study. It is recommended to refer to the official syllabus or consult with your instructor for a comprehensive understanding of the topics covered and the associated study materials.
When is Required Physics syllabus Lenz Law
Lenz’s Law is typically included in the physics syllabus when studying topics related to electromagnetism and electromagnetic induction. The exact timing of when Lenz’s Law is covered in the syllabus can vary depending on the educational institution and the specific curriculum.
In many physics courses, Lenz’s Law is introduced after foundational topics such as magnetic fields, magnetic forces, and electromagnetic induction are covered. Once students have a basic understanding of these concepts, Lenz’s Law is then introduced to explain the direction of the induced current in a conductor.
Typically, Lenz’s Law is covered in the middle to later stages of a physics course that focuses on electromagnetism. It is often taught alongside related topics such as Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction, transformers, electric generators, and practical applications of electromagnetic induction.
To get accurate information about when Lenz’s Law is specifically taught in your course, it is best to refer to the syllabus provided by your educational institution or consult with your instructor. They will be able to provide you with the specific timing and sequence of topics covered in your physics syllabus.
Where is Required Physics syllabus Lenz Law
The inclusion of Lenz’s Law in the required physics syllabus can vary depending on the educational system, curriculum, and level of study. In general, Lenz’s Law is typically found in physics courses that cover electromagnetism and electromagnetic induction.
The specific location of Lenz’s Law within the syllabus will depend on the organization and structure of the course. However, it is commonly taught after introducing foundational concepts such as magnetic fields, magnetic forces, and basic principles of electromagnetic induction.
Lenz’s Law is often discussed in the context of Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction, which describes how a changing magnetic field induces an electromotive force (emf) in a conductor. Lenz’s Law is then introduced to explain the direction of the induced current based on the change in magnetic flux.
To determine the exact placement of Lenz’s Law within your physics syllabus, it is recommended to refer to the official syllabus provided by your educational institution or consult with your instructor. They will have the specific information regarding the sequencing and organization of topics in your course.
How is Required Physics syllabus Lenz Law
The inclusion and coverage of Lenz’s Law in the required physics syllabus may vary depending on the educational institution and the specific curriculum. However, here is a general outline of how Lenz’s Law is typically taught in a physics course:
- Introduction to Electromagnetism: The course will usually begin with an introduction to electromagnetism, covering basic concepts such as electric and magnetic fields, magnetic forces, and the behavior of charged particles in magnetic fields.
- Electromagnetic Induction: The syllabus will then move on to electromagnetic induction, which includes topics like Faraday’s Law and Lenz’s Law. Faraday’s Law explains how a changing magnetic field induces an electromotive force (emf) in a conductor, and Lenz’s Law describes the direction of the induced current.
- Lenz’s Law: Lenz’s Law is introduced as a principle that states the induced current in a conductor will flow in a direction that opposes the change in the magnetic field that caused it. Students will learn about the relationship between the changing magnetic field, the induced current, and the magnetic flux.
- Applications of Lenz’s Law: The syllabus may cover various applications and phenomena related to Lenz’s Law. This can include the use of Lenz’s Law in electric generators, transformers, eddy currents, electromagnetic braking, and electromagnetic induction experiments.
- Problem-solving and Analysis: Students will engage in problem-solving exercises and analyze practical scenarios to apply Lenz’s Law and understand its implications in real-world situations.
It’s important to note that the level of depth and specific subtopics covered may vary depending on the course and curriculum. For a more detailed understanding of how Lenz’s Law is covered in your specific physics syllabus, referring to the official syllabus provided by your educational institution or consulting with your instructor is recommended.
Case Study on Physics syllabus Lenz Law
As an AI language model, I can provide a brief example of how Lenz’s Law might be incorporated into a physics syllabus through a case study:
Case Study: Electromagnetic Induction and Lenz’s Law
Course: Physics 202
Module: Electromagnetism
Topic: Lenz’s Law and its Applications
- Introduction (2 lectures):
- Overview of electromagnetism and magnetic fields.
- Introduction to electromagnetic induction and Faraday’s Law.
- Motivation for understanding Lenz’s Law.
- Lenz’s Law (3 lectures):
- Definition and statement of Lenz’s Law.
- Understanding the concept of magnetic flux and its relation to Lenz’s Law.
- Explanation of how Lenz’s Law provides a direction for the induced current.
- Mathematical formulation and examples illustrating Lenz’s Law.
- Applications of Lenz’s Law (4 lectures):
- Electric generators: Exploring how Lenz’s Law is utilized in the generation of electricity through rotating coils in a magnetic field.
- Transformers: Understanding the role of Lenz’s Law in the operation of transformers, including step-up and step-down principles.
- Eddy currents: Exploring the formation and effects of eddy currents in conducting materials due to changing magnetic fields.
- Electromagnetic braking: Discussing how Lenz’s Law is utilized in electromagnetic braking systems for decelerating moving objects.
- Practical Demonstrations and Experiments (2 practical sessions):
- Conducting hands-on experiments to observe and verify Lenz’s Law.
- Demonstrations of electromagnetic induction and the applications of Lenz’s Law.
- Problem-solving and Analysis (2 lectures):
- Solving numerical problems related to Lenz’s Law, electromagnetic induction, and its applications.
- Analyzing real-life scenarios to understand the practical implications of Lenz’s Law.
- Review and Assessment (1 lecture):
- Review of key concepts, equations, and applications related to Lenz’s Law.
- Assessment through quizzes and a final examination.
Note: This case study is a fictional example and does not represent the specific structure or duration of any real physics course. The actual syllabus and curriculum may vary depending on the educational institution and course requirements.
White paper on Physics syllabus Lenz Law
Title: Lenz’s Law: Understanding Electromagnetic Induction and its Applications
Abstract: This white paper provides a comprehensive exploration of Lenz’s Law, a fundamental principle in electromagnetism that governs the behavior of induced currents in the presence of changing magnetic fields. Lenz’s Law states that the induced current in a conductor will flow in a direction that opposes the change in magnetic flux that caused it. This paper discusses the origins of Lenz’s Law, its mathematical formulation, and its practical applications in various fields.
- Introduction
- Overview of electromagnetic induction and its significance in modern technology.
- Introduction to Lenz’s Law as a guiding principle for understanding induced currents.
- Historical Background
- The contribution of Heinrich Lenz in formulating Lenz’s Law.
- Development of the concept in relation to the laws of electromagnetism.
- Understanding Lenz’s Law
- Definition and statement of Lenz’s Law.
- Explanation of the concept of magnetic flux and its relationship with Lenz’s Law.
- Mathematical formulation of Lenz’s Law and its application to determine the direction of induced currents.
- Practical Applications
- Electric Generators: Examining the use of Lenz’s Law in the generation of electricity through electromagnetic induction.
- Transformers: Understanding how Lenz’s Law plays a crucial role in the functioning of transformers.
- Eddy Currents: Exploring the formation and effects of eddy currents in conducting materials.
- Electromagnetic Braking: Discussing the application of Lenz’s Law in braking systems for deceleration.
- Experimental Verification
- Description of experimental setups and demonstrations to observe the effects of Lenz’s Law.
- Analysis of experimental results and correlation with theoretical predictions.
- Advanced Topics
- Time-varying Magnetic Fields: Investigating the behavior of Lenz’s Law in the presence of rapidly changing magnetic fields.
- Magnetic Shielding: Understanding how Lenz’s Law can be used to mitigate the effects of external magnetic fields.
- Practical Considerations and Limitations
- Factors influencing the magnitude and direction of induced currents.
- Limitations and challenges associated with the practical application of Lenz’s Law.
- Conclusion
- Recapitulation of the key concepts and applications of Lenz’s Law.
- Future directions for research and potential advancements in the understanding and utilization of Lenz’s Law.
This white paper serves as a comprehensive resource for researchers, students, and professionals seeking a deeper understanding of Lenz’s Law and its practical implications in various fields. By delving into the theoretical foundations, experimental verifications, and real-world applications, this paper aims to enhance knowledge and stimulate further exploration in the realm of electromagnetic induction and Lenz’s Law.