In mathematics, the range of a function is the set of all possible output values that the function can produce when it is applied to the elements of its domain. It is sometimes called the image of the function. The range is a subset of the codomain, which is the set of all possible output values that the function can produce.
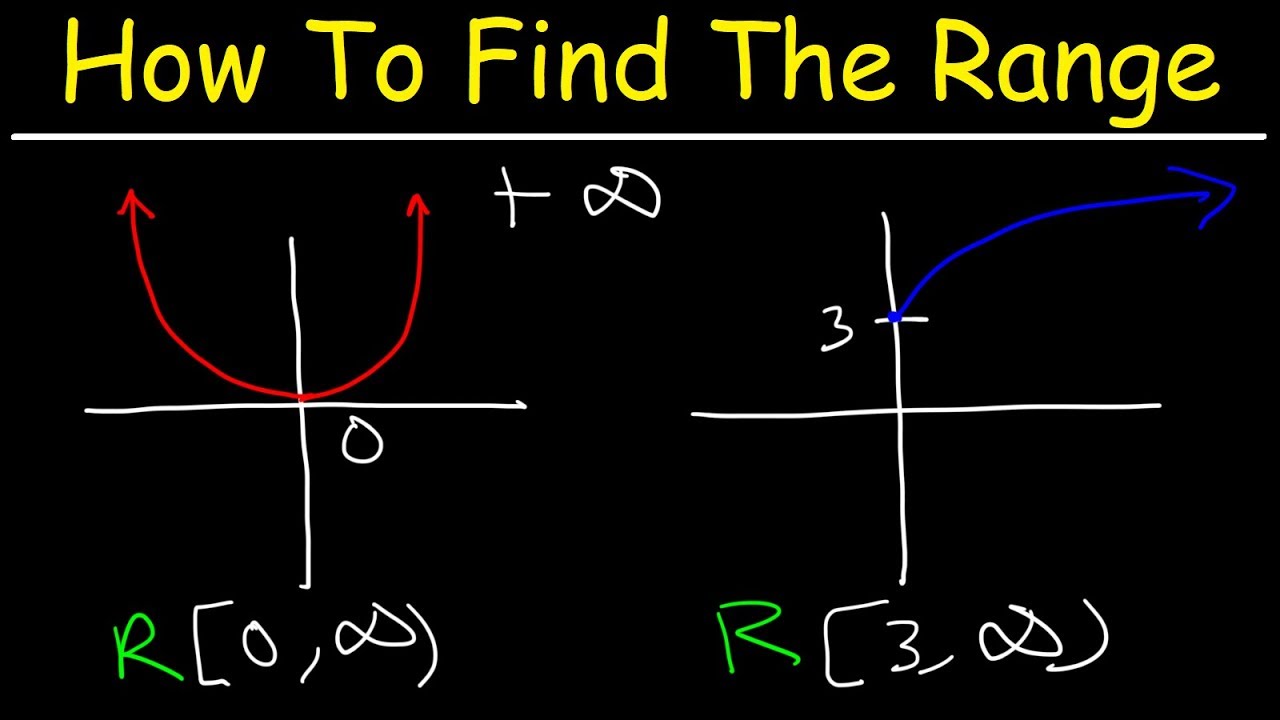
For example, consider the function f(x) = x^2, with domain set to all real numbers. The output values that this function can produce are non-negative real numbers, since the square of any real number is non-negative. Therefore, the range of this function is the set of non-negative real numbers, which is a subset of the codomain, the set of all real numbers.
The range of a function can be determined by analyzing its behavior on the domain. In some cases, the range can be explicitly calculated by finding all the possible output values of the function for each element of the domain. However, in other cases, it may be difficult or impossible to determine the range explicitly.
The range is an important concept in mathematics because it provides information about the behavior of a function and its relationship to other mathematical objects. It can be used to identify important properties of a function, such as its continuity, monotonicity, and periodicity. In addition, the range can be used to define the inverse of a function, which is a function that maps the output values of the original function back to their corresponding input values.
It is important to note that the range of a function may not be equal to its codomain. A function may have a smaller range than its codomain if some elements of the codomain are not outputted by the function for any elements of its domain. In this case, the function is said to be not surjective or onto. A function that has the same range as its codomain is called surjective or onto.
Range (statistics)
In measurements, the scope of a bunch of information is the distinction between the biggest and littlest values, the consequence of deducting the example most extreme and least. It is communicated in similar units as the information.
In clear measurements, range is the size of the littlest stretch which contains every one of the information and gives a sign of factual scattering. Since it just relies upon two of the perceptions, it is most valuable in addressing the scattering of little information sets.
Who is Required range of functions
“Required range of functions” is not a person or a concept that I am aware of in mathematics. The range of a function is a mathematical concept that describes the set of all possible output values that a function can produce when it is applied to the elements of its domain. It is sometimes called the image of the function. If you have any further questions about the concept of range of functions, I would be happy to help.
When is Required range of functions
The concept of range of functions is applicable whenever we are working with a mathematical function. A function is a rule that assigns each element from one set, called the domain, to exactly one element from another set, called the range or codomain.
The range of a function is the set of all possible output values that the function can produce when it is applied to the elements of its domain. It is an important concept in mathematics because it provides information about the behavior of a function and its relationship to other mathematical objects.
Whenever we are working with a mathematical function, we can consider its range to help us understand its properties and behavior. For example, the range can be used to identify important properties of a function, such as its continuity, monotonicity, and periodicity. It can also be used to define the inverse of a function, which is a function that maps the output values of the original function back to their corresponding input values.
Where is Required range of functions
The concept of range of functions is a mathematical concept that can be applied in various fields of mathematics such as algebra, calculus, and analysis. It is a fundamental concept that is used to describe the behavior of functions and their relationships to other mathematical objects.
The concept of range of functions is not limited to any particular location or physical setting. It is a universal mathematical concept that can be applied anywhere and anytime, as long as we are working with mathematical functions.
In terms of its practical applications, the concept of range of functions is used in a variety of fields such as physics, engineering, economics, and computer science. For example, in physics, the range of a function can be used to describe the possible values of a physical quantity based on the input parameters of the function. In economics, the range of a demand function can be used to analyze the behavior of a market under different conditions. In computer science, the range of a function can be used to determine the output values of a computer program for different inputs.
How is Required range of functions
The range of a function is determined by analyzing its behavior on the domain. In general, to find the range of a function, we need to determine all the possible output values that the function can produce for each element of the domain.
One way to determine the range of a function is to use algebraic methods such as solving equations or inequalities. For example, if we have a function f(x) = x^2, and we want to find its range, we can use algebra to determine that the minimum value of f(x) is 0, and there is no maximum value. Therefore, the range of the function is [0, infinity).
Another way to determine the range of a function is to use graphical methods such as plotting the function on a graph and examining its behavior. For example, if we have a function f(x) = sin(x), and we want to find its range, we can plot the function on a graph and observe that the maximum and minimum values of the function are 1 and -1, respectively. Therefore, the range of the function is [-1, 1].
In some cases, the range of a function can be determined by finding the inverse of the function. The inverse of a function maps the output values of the original function back to their corresponding input values. Therefore, if we know the inverse of a function, we can determine the range of the original function by analyzing the domain of its inverse.
It is important to note that determining the range of a function can be challenging in some cases, especially for more complex functions or functions with unusual behavior. In these cases, mathematical techniques such as calculus or numerical methods may be necessary to determine the range of the function.
Case Study on range of functions
Here’s a simple case study on range of functions:
Consider the function f(x) = x^2. To find the range of this function, we need to determine all the possible output values that the function can produce for each element of the domain. In this case, the domain of the function is all real numbers.
To determine the range of the function, we can use algebraic methods. We start by noting that f(x) is always non-negative, since x^2 is positive or zero for all values of x. Therefore, the minimum value of f(x) is 0, which occurs when x = 0.
To find the maximum value of f(x), we can try to solve the equation f(x) = k, where k is some constant. We get x^2 = k, which implies that x = +/- sqrt(k). Therefore, the function can produce any non-negative real number as an output. In other words, the range of the function is [0, infinity).
We can also verify this result by plotting the function on a graph. The graph of f(x) = x^2 is a parabola that opens upwards, with its vertex at the origin. This confirms that the minimum value of the function is 0, and there is no maximum value.
The range of the function is an important concept because it describes the set of all possible output values that the function can produce. In this case, the range tells us that the function can produce any non-negative real number as an output, which is important information when analyzing the behavior of the function or using it in other mathematical contexts.
White paper on range of functions
Introduction: The concept of range of functions is an important mathematical concept that is used in a variety of fields. The range of a function is the set of all possible output values that the function can produce for each element of its domain. It is a fundamental concept that helps us to understand the behavior of functions and their relationships to other mathematical objects. This white paper will provide a detailed overview of the range of functions, including its definition, calculation methods, and practical applications.
Definition: The range of a function is the set of all possible output values that the function can produce for each element of its domain. In other words, the range of a function is the set of all y-values that are produced by the function. The range is often denoted as R(f) or Im(f), where f is the function.
Calculation methods: There are several methods for calculating the range of a function, depending on the complexity of the function and the available tools. Some common methods include:
- Algebraic methods: Algebraic methods involve manipulating the function algebraically to determine its range. For example, if we have a function f(x) = x^2, we can use algebra to determine that the minimum value of f(x) is 0, and there is no maximum value. Therefore, the range of the function is [0, infinity).
- Graphical methods: Graphical methods involve plotting the function on a graph and examining its behavior to determine its range. For example, if we have a function f(x) = sin(x), we can plot the function on a graph and observe that the maximum and minimum values of the function are 1 and -1, respectively. Therefore, the range of the function is [-1, 1].
- Inverse function: In some cases, the range of a function can be determined by finding the inverse of the function. The inverse of a function maps the output values of the original function back to their corresponding input values. Therefore, if we know the inverse of a function, we can determine the range of the original function by analyzing the domain of its inverse.
Practical applications: The range of a function has many practical applications in various fields of mathematics, science, and engineering. Some common applications include:
- Physics: The range of a function can be used to describe the possible values of a physical quantity based on the input parameters of the function. For example, the range of a projectile motion function can be used to determine the maximum height and range of a projectile.
- Engineering: The range of a function can be used to analyze the behavior of a system under different conditions. For example, the range of a demand function can be used to analyze the behavior of a market under different conditions.
- Computer science: The range of a function can be used to determine the output values of a computer program for different inputs. For example, the range of a sorting algorithm can be used to determine the maximum and minimum values that can be sorted.
Conclusion: In conclusion, the range of functions is an important mathematical concept that helps us to understand the behavior of functions and their relationships to other mathematical objects. The range is the set of all possible output values that the function can produce for each element of its domain. There are several methods for calculating the range of a function, including algebraic, graphical, and inverse methods. The range of a function has many practical applications in various fields, including physics, engineering, and computer science.
