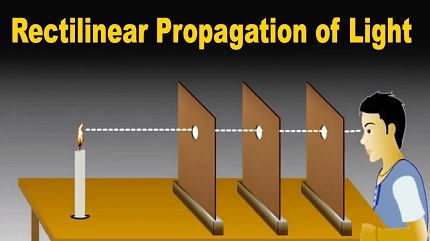
Rectilinear propagation of light refers to the phenomenon where light travels in straight lines in a uniform medium such as air, water, or vacuum. This is a fundamental property of light and is a consequence of the wave nature of light. When light travels through a medium with a uniform refractive index, it experiences no change in direction as long as it travels in a straight line.
The principle of rectilinear propagation of light is the basis of several optical instruments like mirrors, lenses, and prisms. These instruments work by manipulating the path of light through refraction, reflection, or a combination of both. The path of light is calculated by using Snell’s law and the laws of reflection, which are based on the principle of rectilinear propagation.
However, in some cases, light may not travel in a straight line due to the presence of obstacles or irregularities in the medium through which it is passing. This can result in phenomena such as diffraction, scattering, and refraction, which cause the light to bend or spread out. Nonetheless, in the absence of such disturbances, light will always travel in a straight line, as per the principle of rectilinear propagation of light.
What is Rectilinear propagation of light
Rectilinear propagation of light is the principle that light travels in straight lines in a uniform medium, such as air, water, or vacuum. This phenomenon is one of the fundamental properties of light and is a result of its wave-like nature.
When light travels through a medium with a uniform refractive index, it experiences no change in direction as long as it travels in a straight line. This principle is the basis of several optical instruments such as mirrors, lenses, and prisms, which manipulate the path of light through reflection and refraction.
However, in some cases, light may not travel in a straight line due to the presence of obstacles or irregularities in the medium through which it is passing. This can result in phenomena such as diffraction, scattering, and refraction, which cause the light to bend or spread out. Nonetheless, in the absence of such disturbances, light will always travel in a straight line, as per the principle of rectilinear propagation of light.
When is Rectilinear propagation of light
The principle of rectilinear propagation of light is observed when light travels through a uniform medium, such as air, water, or vacuum. In such a medium, light travels in a straight line and maintains its direction unless it encounters an obstacle or a boundary between two media with different refractive indices.
This principle is fundamental to optics and is used in the design of optical instruments such as mirrors, lenses, and prisms, which manipulate the path of light through reflection and refraction. It is also the reason why shadows have sharp edges and why we can see distant objects clearly, assuming there is no interference from atmospheric conditions such as fog or smog.
However, when light encounters an obstacle or a boundary between two media with different refractive indices, it may deviate from its original path due to diffraction, refraction, or reflection. In such cases, the principle of rectilinear propagation of light is no longer observed.
Where is Rectilinear propagation of light
The principle of rectilinear propagation of light is observed in any uniform medium through which light can travel. This includes air, water, and vacuum, among other media with a uniform refractive index.
For example, light travels in straight lines in air, which is why we can see distant objects clearly and shadows have sharp edges. In water, light also travels in straight lines, but its speed and direction may change due to the refractive index of water being different from that of air. In vacuum, light travels in straight lines at a constant speed of approximately 299,792,458 meters per second, which is the speed of light in a vacuum.
The principle of rectilinear propagation of light is fundamental to optics and is used in the design of many optical devices, such as cameras, telescopes, and microscopes. It is also an essential concept in the study of physics and is used to explain the behavior of light in various situations.
How is Rectilinear propagation of light
Rectilinear propagation of light is a phenomenon that occurs due to the wave-like nature of light. When light travels through a medium with a uniform refractive index, it experiences no change in direction as long as it travels in a straight line.
The principle of rectilinear propagation of light can be explained using two laws:
- The Law of Reflection: When light falls on a smooth surface, it is reflected at an angle that is equal to the angle of incidence.
- Snell’s Law: When light travels from one medium to another, its direction changes due to the difference in the refractive indices of the two media. Snell’s law relates the angle of incidence, the angle of refraction, and the refractive indices of the two media.
These laws govern the path of light as it travels through a uniform medium, enabling us to predict its behavior and design optical instruments such as mirrors, lenses, and prisms.
However, when light encounters an obstacle or a boundary between two media with different refractive indices, it may deviate from its original path due to diffraction, refraction, or reflection. In such cases, the principle of rectilinear propagation of light is no longer observed.
Nomenclature of Rectilinear propagation of light
The term “rectilinear propagation of light” refers to the principle that light travels in straight lines in a uniform medium. The term can be broken down into its constituent parts:
- “Rectilinear” refers to the property of traveling in straight lines.
- “Propagation” refers to the act of spreading or moving through a medium.
- “Light” refers to electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye.
The concept of rectilinear propagation of light is also known as the “law of rectilinear propagation” or the “law of straight-line propagation.” It is a fundamental principle of optics and is used in the design of many optical devices.
In addition to the term “rectilinear propagation of light,” there are several related terms that are commonly used in the study of optics, including:
- Refraction: the bending of light as it passes through a medium with a different refractive index.
- Reflection: the bouncing of light off a surface.
- Diffraction: the bending of light as it passes through a small aperture or around an obstacle.
- Scattering: the redirection of light in different directions as it interacts with particles in a medium.
These terms are all related to the behavior of light as it travels through a medium, and they are used to describe the various phenomena that can occur when light interacts with matter.
Case Study on Rectilinear propagation of light
One example of rectilinear propagation of light can be observed in the formation of shadows. When an object blocks the path of light, it creates a region of darkness behind it, which is known as a shadow. The edges of the shadow are sharp and well-defined, which is a result of the rectilinear propagation of light.
To understand this phenomenon, consider a point source of light emitting rays in all directions. When a flat object, such as a cardboard, is placed in the path of the light, the rays that hit the object are blocked, while the rays that pass to the sides of the object continue in straight lines. This creates a region of darkness behind the object, which is the shadow. The edges of the shadow are well-defined because the light that passes around the object continues in straight lines and does not bend or spread out significantly.
This principle of rectilinear propagation of light is used in photography, where shadows play an important role in creating depth and contrast in an image. Photographers often use artificial lighting to create shadows of different shapes and sizes, which can add interest and drama to the composition.
Another example of rectilinear propagation of light can be observed in the formation of sun rays. When the sun is partially obscured by clouds or other objects, the rays of light that pass through gaps or openings in the obstruction continue in straight lines and create visible beams of light that radiate outward from the sun. These rays are a result of the rectilinear propagation of light and can be observed in many different natural settings, such as sunrise and sunset, as well as in urban environments where light passes through narrow openings between buildings.
White paper on Rectilinear propagation of light
Introduction
Rectilinear propagation of light is a fundamental principle of optics that describes the behavior of light as it travels through a uniform medium in straight lines. This principle has been observed and studied for centuries and has played a crucial role in the development of optical devices such as cameras, telescopes, and microscopes. In this white paper, we will explore the concept of rectilinear propagation of light in detail, including its definition, history, applications, and limitations.
Definition
Rectilinear propagation of light refers to the property of light traveling in straight lines in a uniform medium. This principle is a consequence of the wave-like nature of light, which allows it to propagate through space as a series of oscillating electric and magnetic fields. When light travels through a medium with a uniform refractive index, it experiences no change in direction as long as it travels in a straight line.
History
The principle of rectilinear propagation of light was first described by the ancient Greek philosopher Euclid in the 4th century BCE. He observed that light travels in straight lines and noted that the path of light can be altered by reflection or refraction. The ancient Greeks also conducted experiments to measure the speed of light, including the famous experiment conducted by Eratosthenes in the 3rd century BCE, in which he measured the angle of the sun’s rays at two different locations and used the difference to calculate the circumference of the earth.
The concept of rectilinear propagation of light was further developed by medieval Islamic scholars, including Ibn al-Haytham, who conducted experiments to study the behavior of light and developed a theory of vision based on the rectilinear propagation of light. This theory was later adopted and expanded upon by European scientists such as Kepler, Descartes, and Newton, who developed the modern theory of optics based on the wave-like nature of light.
Applications
The principle of rectilinear propagation of light has many practical applications in optics and the design of optical devices. For example, it is used in the design of lenses, mirrors, and prisms, which manipulate the path of light to create images, magnify objects, or split light into its component colors. The principle of rectilinear propagation of light is also used in the design of fiber optic cables, which use total internal reflection to transmit light over long distances without loss of signal.
Rectilinear propagation of light is also an important concept in photography, where it is used to create shadows, depth, and contrast in images. Photographers often use artificial lighting to create shadows of different shapes and sizes, which can add interest and drama to the composition.
Limitations
While the principle of rectilinear propagation of light is a useful tool in optics and the design of optical devices, it has limitations. When light encounters an obstacle or a boundary between two media with different refractive indices, it may deviate from its original path due to diffraction, refraction, or reflection. In such cases, the principle of rectilinear propagation of light is no longer observed, and the path of light may become more complex or diffuse.
Conclusion
Rectilinear propagation of light is a fundamental principle of optics that describes the behavior of light as it travels through a uniform medium in straight lines. This principle has been observed and studied for centuries and has played a crucial role in the development of optical devices and our understanding of the nature of light. While it has limitations, the principle of rectilinear propagation of light remains a powerful tool for scientists and engineers working in the field of optics and optical design.
