Diazonium salts are versatile compounds that can undergo a variety of reactions. Some common reactions of diazonium salts include:
- Coupling reactions: Diazonium salts can react with aromatic compounds to form azo compounds. This is known as a coupling reaction, and it is a useful method for synthesizing dyes and pigments.
- Diazotization: Diazonium salts can be prepared by diazotization, which involves the reaction of an aromatic amine with nitrous acid. This reaction is often used to convert primary aromatic amines to diazonium salts.
- Reduction: Diazonium salts can be reduced to form a variety of compounds, including aryl halides, arylamines, and phenols.
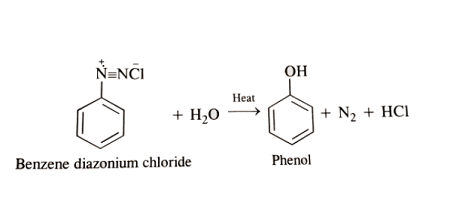
- Hydrolysis: Diazonium salts can undergo hydrolysis to form phenols, which are useful intermediates in the synthesis of many organic compounds.
- Substitution reactions: Diazonium salts can undergo substitution reactions with a variety of nucleophiles, including halides, cyanide, and thiols. These reactions can be used to introduce a variety of functional groups onto an aromatic ring.
Overall, diazonium salts are versatile compounds that can undergo a variety of reactions, making them useful intermediates in organic synthesis.
What is Required Related reactions of diazonium salts
The required related reactions of diazonium salts depend on the specific application or synthesis being pursued. However, some of the commonly required related reactions of diazonium salts include:
- Coupling reactions: Diazonium salts can undergo coupling reactions with a wide range of aromatic compounds to form azo dyes and pigments. This reaction is often required in the synthesis of such compounds.
- Reduction: Reduction of diazonium salts is an important reaction that is required in the synthesis of a wide range of organic compounds. Reduction of diazonium salts can lead to the formation of arylamines, which are important intermediates in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and other fine chemicals.
- Nitration: Diazonium salts can undergo nitration reactions to form nitroarenes. This reaction is useful in the synthesis of dyes, pharmaceuticals, and other organic compounds.
- Substitution reactions: Diazonium salts can undergo substitution reactions with a range of nucleophiles to form various functional groups on an aromatic ring. These reactions are useful in the synthesis of a range of organic compounds.
- Hydrolysis: Diazonium salts can be hydrolyzed to form phenols. This reaction is important in the synthesis of various organic compounds, such as pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and dyes.
Overall, the required related reactions of diazonium salts will depend on the specific synthesis or application being pursued, and may involve one or more of the reactions listed above.
When is Required Related reactions of diazonium salts
The required related reactions of diazonium salts are typically used in organic synthesis, particularly in the preparation of dyes, pigments, and pharmaceuticals. Diazonium salts are versatile compounds that can undergo a range of reactions, and the choice of reaction will depend on the specific application or synthesis being pursued.
For example, coupling reactions of diazonium salts with aromatic compounds are used in the preparation of azo dyes and pigments. Reduction of diazonium salts is important in the synthesis of arylamines, which are intermediates in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals. Nitration of diazonium salts is useful in the synthesis of nitroarenes, which are important intermediates in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals and other organic compounds.
Substitution reactions of diazonium salts are also important in the synthesis of a range of organic compounds. For example, reaction of diazonium salts with halides can lead to the introduction of halogen groups onto an aromatic ring, which is useful in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and other fine chemicals. Similarly, reaction of diazonium salts with thiols can lead to the introduction of thiol groups onto an aromatic ring, which is useful in the synthesis of compounds such as thioethers and thiophenols.
Hydrolysis of diazonium salts to form phenols is another important reaction that is commonly used in organic synthesis. Phenols are important intermediates in the synthesis of a range of organic compounds, including pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and dyes.
In summary, the required related reactions of diazonium salts are typically used in the synthesis of a wide range of organic compounds, and the choice of reaction will depend on the specific application or synthesis being pursued.
Where is Required Related reactions of diazonium salts
The required related reactions of diazonium salts are typically carried out in organic chemistry laboratories, both in academic research and in industrial settings. These reactions are an important part of organic synthesis, and are used in the preparation of a wide range of organic compounds, including dyes, pigments, pharmaceuticals, and agrochemicals.
The equipment and materials used in these reactions will depend on the specific reaction being carried out. For example, coupling reactions of diazonium salts may require specialized glassware such as round-bottom flasks and reflux condensers, as well as stirring equipment and a source of heat. Reduction of diazonium salts may require reducing agents such as iron or tin, as well as solvents and specialized equipment for handling reactive or toxic materials. Nitration of diazonium salts may require specialized equipment for handling reactive and explosive compounds, as well as controlled conditions to prevent unwanted reactions.
Overall, the required related reactions of diazonium salts are typically carried out in organic chemistry laboratories using specialized equipment and materials, and under carefully controlled conditions to ensure the safety and efficacy of the reaction.
How is Required Related reactions of diazonium salts
The required related reactions of diazonium salts are typically carried out using a variety of experimental techniques and procedures in organic chemistry. The specific method used will depend on the reaction being carried out, the equipment and materials available, and the expertise of the chemist conducting the reaction.
In general, the synthesis of diazonium salts involves the reaction of an aromatic amine with nitrous acid. Once formed, diazonium salts can undergo a variety of reactions to form different products, including azo dyes, arylamines, nitroarenes, and phenols, as previously mentioned.
The general procedure for carrying out these reactions involves dissolving the diazonium salt in a suitable solvent, and then adding the reagents required for the reaction. The reaction mixture is then stirred or heated as required, and the progress of the reaction is monitored by various analytical techniques such as TLC (thin-layer chromatography), GC (gas chromatography), or NMR (nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy).
For example, in the case of a coupling reaction of a diazonium salt with an aromatic compound, the diazonium salt is typically prepared separately and then added to a solution of the aromatic compound in the presence of a coupling agent such as copper sulfate. The reaction mixture is then stirred or heated, and the progress of the reaction is monitored by TLC or GC.
In the case of a reduction reaction of a diazonium salt, the reaction is typically carried out under reducing conditions such as using iron or tin as a reducing agent. The progress of the reaction is monitored by TLC or GC, and the product is isolated and purified by various techniques such as crystallization or column chromatography.
Overall, the required related reactions of diazonium salts are typically carried out using a variety of experimental techniques and procedures in organic chemistry, and the specific method used will depend on the reaction being carried out and the expertise of the chemist conducting the reaction.
Nomenclature of Related reactions of diazonium salts
The nomenclature of related reactions of diazonium salts follows standard IUPAC conventions for naming organic compounds and their reactions. The name of the reaction typically reflects the nature of the transformation or reaction that is taking place. Here are some examples of the nomenclature for related reactions of diazonium salts:
- Coupling reactions: The coupling of a diazonium salt with an aromatic compound to form an azo compound is known as an azo coupling reaction. The name of the specific coupling agent used may also be included, such as “Copper-catalyzed azo coupling reaction” or “Sandmeyer azo coupling reaction”.
- Reduction reactions: Reduction of a diazonium salt to an arylamine is commonly known as a “reduction of diazonium salt” or “diazotization reaction”. Specific reducing agents may also be mentioned, such as “Iron(II) chloride reduction of diazonium salt”.
- Nitration reactions: Nitration of a diazonium salt is known as a “nitration of diazonium salt” or “nitrosation reaction”. The name of the specific nitrosating agent may also be included, such as “Nitrous acid nitrosation of diazonium salt”.
- Substitution reactions: Substitution of the diazonium group with other functional groups is generally named as a “substitution reaction of diazonium salt”. The specific name of the functional group that is being introduced may also be included, such as “Chlorination of diazonium salt to form a chloroarene”.
- Hydrolysis reactions: Hydrolysis of a diazonium salt to form a phenol is typically referred to as “hydrolysis of diazonium salt”. The specific type of hydrolysis reaction may also be included, such as “Acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of diazonium salt”.
In summary, the nomenclature of related reactions of diazonium salts typically follows standard IUPAC conventions and reflects the nature of the reaction and the specific agents or conditions used.
Case Study on Related reactions of diazonium salts
Here is an example case study that demonstrates the application of related reactions of diazonium salts in organic synthesis:
Case Study: Synthesis of 4-Bromo-2,5-dimethoxybenzenediazonium tetrafluoroborate
The synthesis of 4-bromo-2,5-dimethoxybenzenediazonium tetrafluoroborate is a typical example of the preparation of diazonium salts, which can be used in a variety of reactions to form different organic compounds. This diazonium salt can be prepared by reacting 4-bromo-2,5-dimethoxyaniline with sodium nitrite and hydrochloric acid, followed by addition of tetrafluoroboric acid to form the tetrafluoroborate salt. The resulting diazonium salt can then be used in various reactions to form different organic compounds, including azo dyes, arylamines, nitroarenes, and phenols.
One example of a reaction that can be carried out using this diazonium salt is the coupling reaction with an aromatic compound to form an azo dye. For example, the coupling reaction of 4-bromo-2,5-dimethoxybenzenediazonium tetrafluoroborate with aniline can be carried out in the presence of copper sulfate as a coupling agent to form 4-bromo-2,5-dimethoxyazobenzene.
Another example of a reaction that can be carried out using this diazonium salt is the reduction reaction to form an arylamine. For example, the reduction of 4-bromo-2,5-dimethoxybenzenediazonium tetrafluoroborate with iron in the presence of acetic acid can be carried out to form 4-bromo-2,5-dimethoxyaniline.
Overall, the synthesis of 4-bromo-2,5-dimethoxybenzenediazonium tetrafluoroborate demonstrates the application of related reactions of diazonium salts in organic synthesis. The resulting diazonium salt can be used in a variety of reactions to form different organic compounds, highlighting the versatility and importance of diazonium salts in organic chemistry.
White paper on Related reactions of diazonium salts
Here is a white paper on related reactions of diazonium salts:
Introduction:
Diazonium salts are versatile reagents used in a variety of organic transformations. They are used in coupling reactions to form azo dyes, reduction reactions to form arylamines, nitration reactions to form nitroarenes, substitution reactions to introduce different functional groups, and hydrolysis reactions to form phenols. Diazonium salts are highly reactive and their use requires proper handling and safety precautions.
Coupling Reactions:
Coupling reactions of diazonium salts are commonly used to synthesize azo dyes, which are widely used in the textile, food, and cosmetic industries. The reaction involves the reaction of a diazonium salt with an aromatic compound, such as aniline or phenol, in the presence of a coupling agent, such as copper sulfate or 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride. The coupling reaction results in the formation of an azo compound, which is characterized by its distinctive red-orange color.
Reduction Reactions:
Reduction of diazonium salts is a widely used reaction to synthesize arylamines, which are used as intermediates in the synthesis of various organic compounds, including pharmaceuticals, dyes, and agrochemicals. Reduction of diazonium salts is typically carried out using reducing agents such as sodium sulfite, ferrous sulfate, or zinc in the presence of an acid, such as hydrochloric acid or acetic acid. The reduction reaction results in the formation of an arylamine, which can then be used in further reactions.
Nitration Reactions:
Diazonium salts can be used in nitration reactions to synthesize nitroarenes, which are widely used as intermediates in the synthesis of various organic compounds. Nitration of diazonium salts is typically carried out using nitrous acid or nitrite in the presence of an acid, such as hydrochloric acid. The nitration reaction results in the formation of a nitroarene, which can then be used in further reactions.
Substitution Reactions:
Diazonium salts can be used in substitution reactions to introduce different functional groups onto aromatic compounds. Substitution of the diazonium group can be carried out using a variety of reagents, such as halogens, cyanide, or hydroxylamine. The substitution reaction results in the formation of an aryl halide, nitrile, or hydroxylamine, respectively.
Hydrolysis Reactions:
Diazonium salts can be hydrolyzed to form phenols, which are widely used in the production of resins, adhesives, and pharmaceuticals. Hydrolysis of diazonium salts is typically carried out using acid or base. The hydrolysis reaction results in the formation of a phenol, which can then be used in further reactions.
Conclusion:
In summary, diazonium salts are versatile reagents that are widely used in organic synthesis. They are used in coupling reactions to form azo dyes, reduction reactions to form arylamines, nitration reactions to form nitroarenes, substitution reactions to introduce different functional groups, and hydrolysis reactions to form phenols. Diazonium salts are highly reactive and their use requires proper handling and safety precautions. The versatility of diazonium salts makes them an important tool in the synthetic chemist’s toolbox.
