Benzene sulphonation is a chemical reaction that involves the substitution of a hydrogen atom on the benzene ring with a sulfonic acid (-SO3H) group. This reaction is an important industrial process used to produce a variety of organic compounds, including detergents, dyes, and pharmaceuticals.
The reaction typically involves treating benzene with concentrated sulfuric acid (H2SO4) and fuming sulfuric acid (oleum, H2SO4/SO3) as a catalyst. The sulfonation reaction is typically carried out under carefully controlled conditions to minimize the formation of undesirable byproducts.
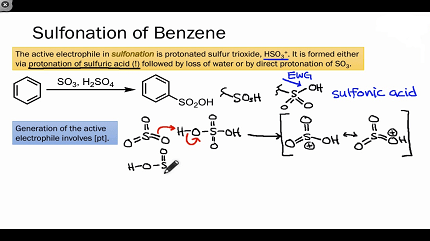
The mechanism of the benzene sulphonation involves the formation of a complex between benzene and sulfuric acid, followed by electrophilic attack by the sulfur trioxide (SO3) generated from the oleum on the benzene ring. This leads to the formation of a sulfonic acid group (-SO3H) attached to the benzene ring.
The sulfonic acid group is a strongly acidic functional group and can undergo various chemical reactions to form a wide range of products. For example, it can be converted to a variety of other functional groups through reactions such as esterification, amidation, and alkylation.
Overall, benzene sulphonation is an important chemical reaction that has significant industrial applications in the production of a wide range of organic compounds.
What is Required Benzene Sulphonation
Benzene sulfonation is a chemical reaction that involves the introduction of a sulfonic acid (-SO3H) group into the benzene ring. This reaction is typically carried out by reacting benzene with sulfuric acid (H2SO4) and an oxidizing agent such as nitric acid (HNO3).
The reaction is typically conducted under carefully controlled conditions, as it can be exothermic and potentially dangerous. The required conditions include maintaining a low temperature (less than 50°C), controlling the addition of the sulfuric acid to prevent the temperature from rising too rapidly, and using an excess of sulfuric acid to ensure that the reaction proceeds to completion.
The product of benzene sulfonation is known as benzenesulfonic acid (also called “sulfobenzene” or “phenylsulfonic acid”), which is a strong acid that is widely used in the production of various chemicals, including detergents, pharmaceuticals, and dyes.
When is Required Benzene Sulphonation
Benzene sulfonation is a versatile reaction that is used in a wide range of industrial applications. Some of the most common uses of benzene sulfonation include:
- Detergent production: Benzenesulfonic acid is a key raw material for the production of alkylbenzenesulfonates, which are used in the manufacture of detergents and cleaning products.
- Pharmaceuticals: Benzenesulfonic acid and its derivatives are used as intermediates in the synthesis of a variety of pharmaceuticals, including antibiotics, antihistamines, and diuretics.
- Dye production: Benzenesulfonic acid is a key intermediate in the production of many dyes, including acid dyes and direct dyes.
- Polymer production: Benzenesulfonic acid is used as a catalyst in the production of certain types of polymer, including polystyrene sulfonate.
Overall, benzene sulfonation is an important industrial process that is used in a variety of applications where the introduction of a sulfonic acid group into a molecule is desired.
Where is Required Benzene Sulphonation
Benzene sulfonation is a widely used chemical reaction that is carried out in various industries around the world. Some of the industries and applications where benzene sulfonation is commonly used include:
- Detergent and cleaning products manufacturing: Benzene sulfonation is used in the production of alkylbenzenesulfonates, which are the key raw material for manufacturing detergents and cleaning products.
- Pharmaceutical manufacturing: Benzene sulfonation is used in the synthesis of a variety of pharmaceuticals, including antibiotics, antihistamines, and diuretics.
- Chemical manufacturing: Benzene sulfonation is used as an intermediate in the production of a variety of chemicals, including dyes, pigments, and surfactants.
- Polymer manufacturing: Benzene sulfonation is used as a catalyst in the production of certain types of polymer, including polystyrene sulfonate.
- Petroleum industry: Benzene sulfonic acid is used as a catalyst in some petroleum refining processes.
Overall, benzene sulfonation is a versatile chemical reaction that is widely used in various industries where the introduction of a sulfonic acid group into a molecule is required.
How is Required Benzene Sulphonation
Benzene sulfonation is a chemical reaction that involves the introduction of a sulfonic acid (-SO3H) group into the benzene ring. This reaction is typically carried out by reacting benzene with sulfuric acid (H2SO4) and an oxidizing agent such as nitric acid (HNO3). The reaction can be summarized as follows:
C6H6 + H2SO4 → C6H5SO3H + H2O
The reaction is typically carried out under carefully controlled conditions, as it can be exothermic and potentially dangerous. The required conditions include maintaining a low temperature (less than 50°C), controlling the addition of the sulfuric acid to prevent the temperature from rising too rapidly, and using an excess of sulfuric acid to ensure that the reaction proceeds to completion. The addition of an oxidizing agent, such as nitric acid, is used to promote the reaction by generating the electrophilic species required for the sulfonation reaction to occur.
After the reaction is complete, the product benzenesulfonic acid is typically separated from the reaction mixture by extraction with water, and then purified by various techniques such as crystallization or distillation.
Overall, benzene sulfonation is an important industrial process that is widely used in the production of various chemicals and materials. The reaction must be carried out under carefully controlled conditions to ensure safety and efficiency.
Production of Benzene Sulphonation
The production of benzene sulfonic acid (benzenesulphonation) is typically carried out on an industrial scale using batch or continuous reactors. The process involves several steps:
- Sulfonation: The first step in the process is the sulfonation of benzene using sulfuric acid and an oxidizing agent, typically nitric acid. The reaction is typically carried out in a reactor vessel equipped with temperature and pressure controls. The reactants are added slowly and carefully to prevent uncontrolled reactions and to maintain a consistent temperature.
- Neutralization: After the sulfonation reaction is complete, the reaction mixture is neutralized with a base such as sodium hydroxide or calcium hydroxide to form the sodium or calcium salt of benzenesulfonic acid.
- Separation and purification: The resulting mixture is then subjected to a series of separation and purification steps, including filtration, distillation, and crystallization, to remove impurities and isolate the pure benzenesulfonic acid.
- Recovery and recycling: Any unreacted benzene and sulfuric acid, as well as the waste stream, are typically recovered and recycled to minimize waste and reduce production costs.
Overall, the production of benzenesulfonic acid is a complex process that requires careful control of the reaction conditions and multiple purification steps to produce a high-quality product. The process is carried out on an industrial scale to meet the demand for this important chemical in various industries such as detergents, pharmaceuticals, and dye production.
Case Study on Benzene Sulphonation
One case study on benzene sulfonation is its use in the production of linear alkylbenzenesulfonates (LAS), which are widely used as a surfactant in the detergent industry.
In this process, benzene is sulfonated with a mixture of sulfuric acid and oleum (fuming sulfuric acid) to produce benzenesulfonic acid. The reaction is exothermic, and the temperature is maintained below 60°C to prevent over-sulfonation and to ensure the product’s desired purity.
After sulfonation, the benzenesulfonic acid is neutralized with an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide to form sodium benzenesulfonate. This product is then reacted with an alkyl halide (typically chlorides or sulfates) to produce linear alkylbenzenesulfonates. The resulting product is then purified and dried to produce a powder that can be used as a surfactant in detergent formulations.
This process is carried out on an industrial scale and is an essential step in the production of many household and industrial cleaning products. The demand for linear alkylbenzenesulfonates is high due to their excellent detergency, biodegradability, and low toxicity, making them a popular choice for use in a wide range of cleaning products.
However, there are some environmental concerns associated with the production of LAS. The process involves the use of toxic chemicals such as sulfuric acid and oleum, which can pose a risk to human health and the environment if not handled correctly. Therefore, there are strict regulations in place to ensure that the production of LAS is carried out safely and responsibly, with waste streams and emissions carefully monitored and controlled.
White paper on Benzene Sulphonation
Here is a white paper on Benzene Sulphonation:
Introduction:
Benzene sulfonation is an important chemical reaction that involves the introduction of a sulfonic acid (-SO3H) group into the benzene ring. It is widely used in the production of various chemicals and materials such as dyes, pharmaceuticals, and detergents. This white paper aims to provide an overview of the benzene sulfonation process, its industrial applications, and the challenges associated with its use.
Benzene Sulfonation Process:
The benzene sulfonation process involves the reaction of benzene with sulfuric acid (H2SO4) and an oxidizing agent such as nitric acid (HNO3). The reaction is typically carried out under carefully controlled conditions to ensure safety and efficiency. The addition of an oxidizing agent is used to generate the electrophilic species required for the sulfonation reaction to occur.
After the reaction is complete, the product benzenesulfonic acid is typically separated from the reaction mixture by extraction with water, and then purified by various techniques such as crystallization or distillation. Any unreacted benzene and sulfuric acid, as well as the waste stream, are typically recovered and recycled to minimize waste and reduce production costs.
Industrial Applications:
Benzene sulfonation is an essential process in the production of many chemicals and materials. One of the most significant industrial applications of benzene sulfonation is in the production of linear alkylbenzenesulfonates (LAS), which are widely used as a surfactant in the detergent industry. The process involves sulfonation of benzene with a mixture of sulfuric acid and oleum to produce benzenesulfonic acid, which is then neutralized with sodium hydroxide and reacted with an alkyl halide to produce LAS. Other applications of benzene sulfonation include the production of dyes, pharmaceuticals, and other chemicals.
Challenges:
Although benzene sulfonation is an essential process, there are some challenges associated with its use. The process involves the use of hazardous chemicals such as sulfuric acid and oleum, which can pose a risk to human health and the environment if not handled correctly. Therefore, there are strict regulations in place to ensure that the production of benzene sulfonic acid is carried out safely and responsibly, with waste streams and emissions carefully monitored and controlled.
Another challenge associated with benzene sulfonation is the production of undesirable by-products such as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). These by-products are highly carcinogenic and can pose a risk to human health and the environment if not properly disposed of.
Conclusion:
Benzene sulfonation is an important chemical reaction that is widely used in the production of various chemicals and materials. The process involves the introduction of a sulfonic acid group into the benzene ring and is typically carried out under carefully controlled conditions to ensure safety and efficiency. Although there are some challenges associated with the use of benzene sulfonation, such as the use of hazardous chemicals and the production of undesirable by-products, these challenges can be overcome through the implementation of strict regulations and the use of appropriate waste management techniques.
