Angle between two lines
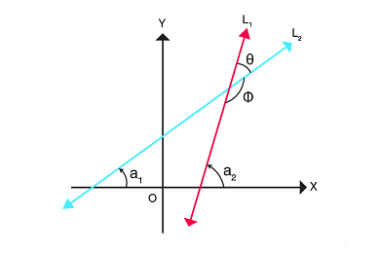
The angle between two lines can be found using the slope of each line. If the slopes of the lines are m1 and m2, then the angle between the lines is given by the formula: θ = arctan(|(m1 – m2)/(1 + m1*m2)|) where arctan is the inverse tangent function. Note that the absolute value is…