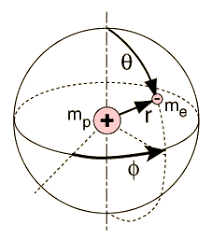
Aufbau Principle
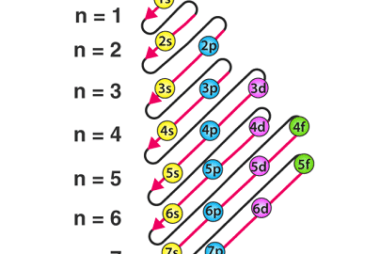
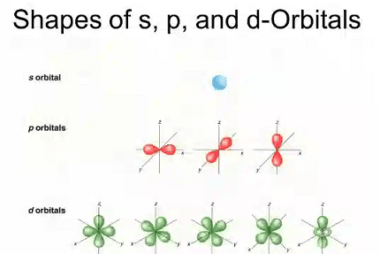
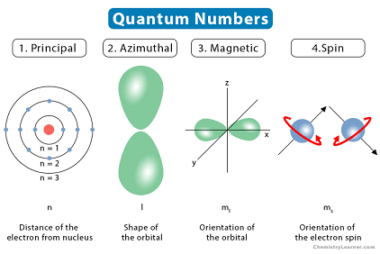
The Aufbau principle, also known as the Aufbau rule, is a fundamental concept in chemistry that explains the order in which electrons fill atomic orbitals in an atom. It is based on the idea that electrons occupy the lowest available energy level or orbital first, before filling higher levels or orbitals. According to the Aufbau…