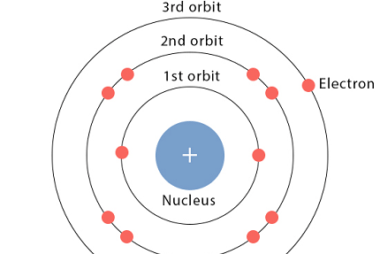
Bohr model
The Bohr model is a simple model of the atom proposed by Danish physicist Niels Bohr in 1913. It was an early attempt to explain the behavior of electrons in an atom and the spectrum of light emitted by atoms. The Bohr model posits that electrons move in circular orbits around the nucleus of an…