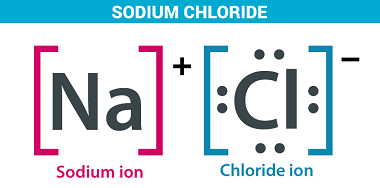
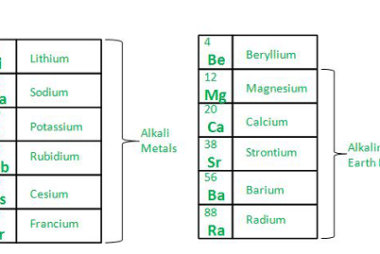
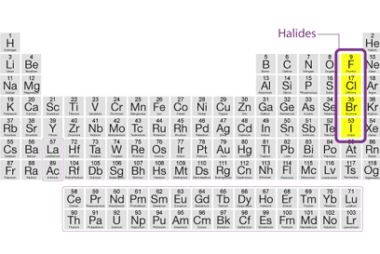
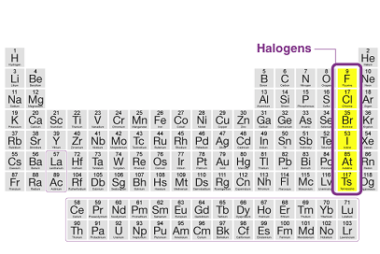
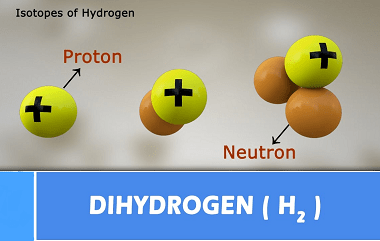
Sodium chloride
Sodium chloride, also known as table salt, is a chemical compound with the formula NaCl. It is an ionic compound consisting of a sodium cation (Na+) and a chloride anion (Cl-). Sodium chloride is one of the most widely used and important chemicals in the world, with a variety of industrial, agricultural, and culinary applications.…