Properties and uses of hydrogen
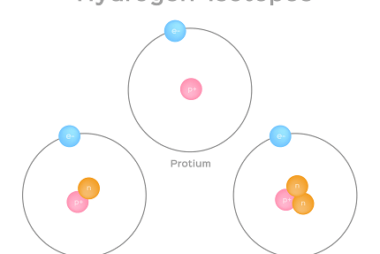
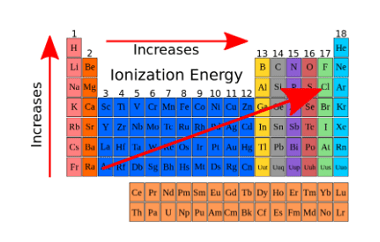
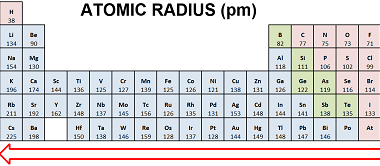
Hydrogen is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas. It is the most abundant element in the universe, constituting about 75% of its elemental mass. Here are some of the properties and uses of hydrogen: Properties: Uses: Overall, hydrogen has a wide range of uses in various industries due to its unique properties, such as its…