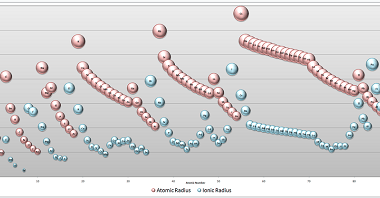
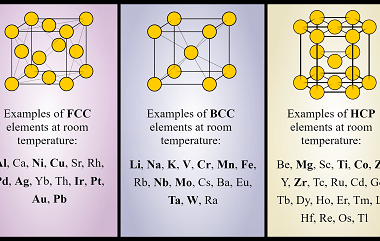
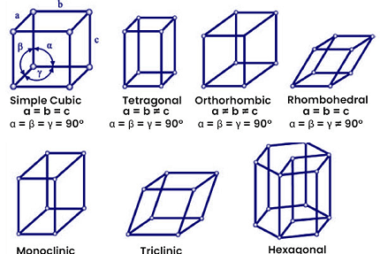
Ionic radii and radius ratio
Ionic radii refers to the size of an ion, which is typically smaller than the size of the corresponding neutral atom due to the gain or loss of one or more electrons. The ionic radius of an ion can be determined by measuring the distance between the nuclei of two ions that are bonded together.…