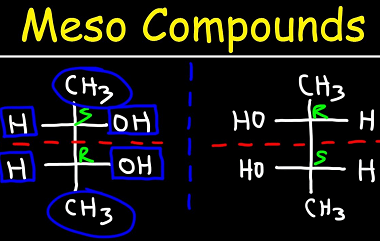
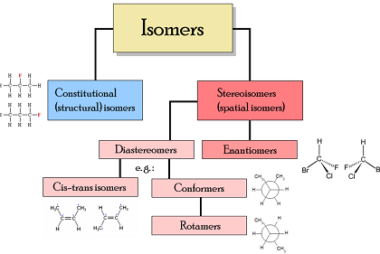
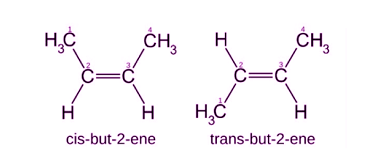
Meso
“Meso” can have several meanings depending on the context: Without more context, it is difficult to determine which meaning of “meso” you are referring to. What is Required Basic Principles of Organic Chemistry Meso There are several basic principles in organic chemistry that are relevant to meso compounds: Overall, a strong foundation in organic chemistry…