Soil pollution
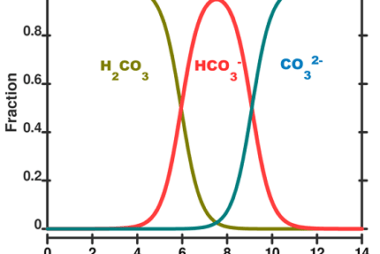
Soil pollution refers to the contamination of soil with harmful substances that can have a detrimental effect on the environment, human health, and the ecosystem. Soil pollution can occur from various sources, including industrial activities, agricultural practices, improper disposal of waste, and natural disasters. Some common contaminants that contribute to soil pollution include heavy metals,…