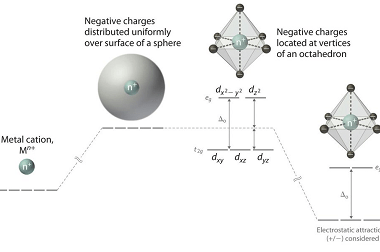
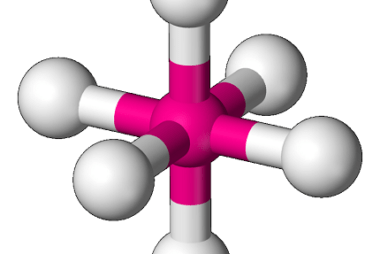
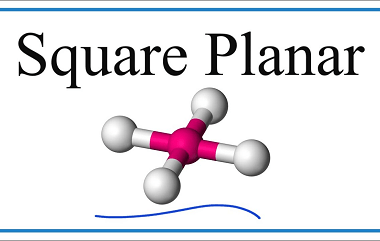
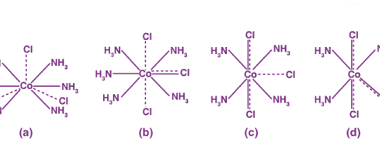
Bonding [VBT and CFT (octahedral and tetrahedral fields)]
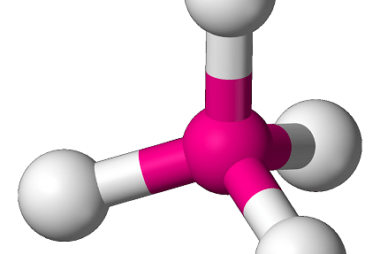
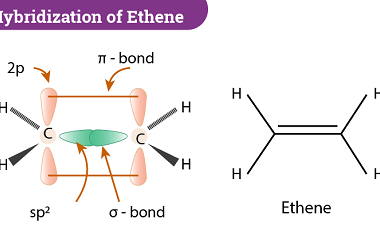
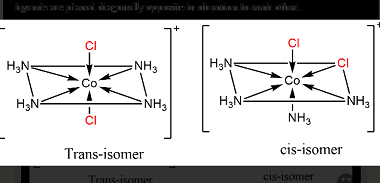
In chemistry, bonding refers to the interactions between atoms that hold them together to form molecules. There are several theories that attempt to explain chemical bonding, including Valence Bond Theory (VBT) and Crystal Field Theory (CFT). Valence Bond Theory proposes that covalent bonds are formed through the sharing of electrons between atoms. This theory describes…