Integrated Course AIIMS-SYLLABUS Chemistry syllabus Extraction of aluminum
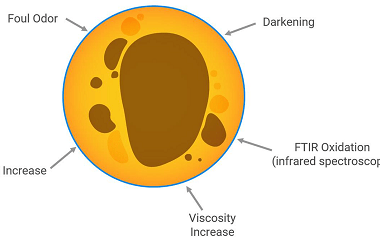
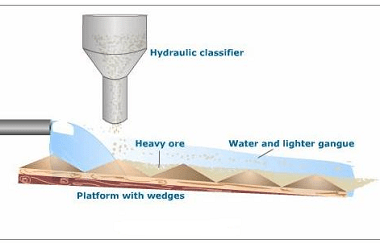
Extraction of aluminum The extraction of aluminum from its ore is a significant topic in chemistry and is often covered in the syllabus of various competitive exams, including the AIIMS entrance exam. The process of extracting aluminum involves several steps and is known as the Hall-Héroult process. Here is a brief overview of the extraction…