Emf of galvanic cells
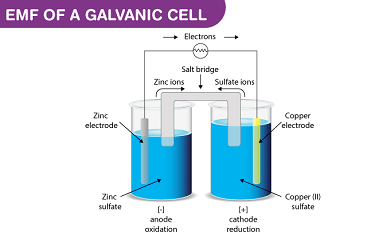
A galvanic cell, also known as a voltaic cell, is an electrochemical cell that converts chemical energy into electrical energy. The cell consists of two electrodes, each with a different reduction potential, that are connected by an electrolyte. The potential difference between the two electrodes is known as the cell potential or electromotive force (EMF)…