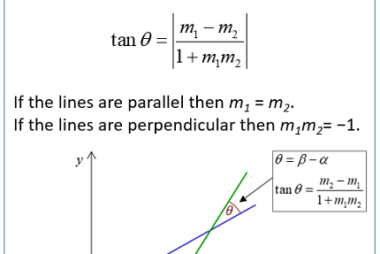
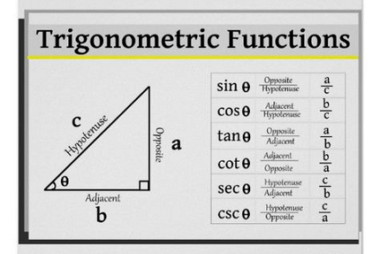
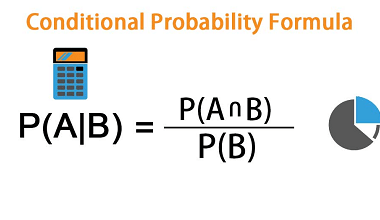
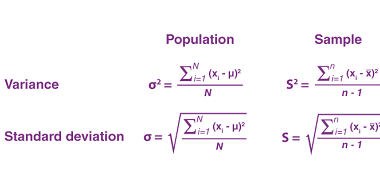Incentre and circumcentre of a triangle
Circumscribed circle In calculation, the encompassed circle or circumcircle of a polygon is a circle that goes through all the vertices of the polygon. The focal point of this circle is known as the circumcenter and its range is known as the circumradius. Few out of every odd polygon has an encompassed circle. A polygon…