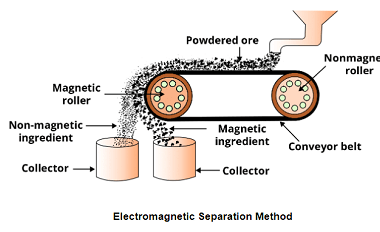
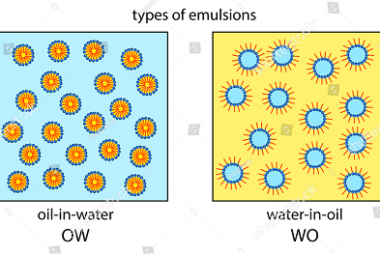
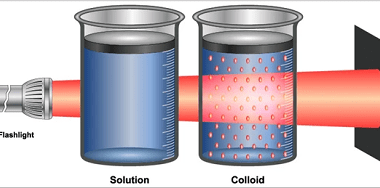
Crash Course AIIMS-SYLLABUS Chemistry syllabus Methods to extract
Methods to extract The AIIMS (All India Institute of Medical Sciences) syllabus for chemistry focuses on the fundamental concepts of the subject. While the specific methods to extract certain substances can vary, here are some commonly covered topics in the AIIMS chemistry syllabus: When it comes to methods of extraction, the AIIMS chemistry syllabus may…