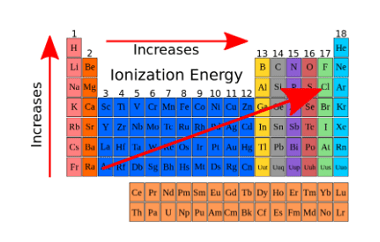
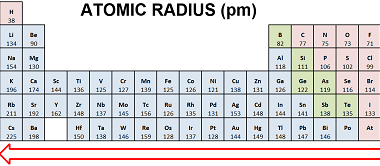
Isotopes
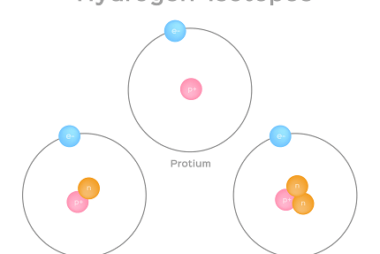
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei. This means that isotopes of a particular element have the same atomic number but different atomic masses. For example, carbon-12, carbon-13, and carbon-14 are all isotopes of carbon, with 6 protons but 6,…