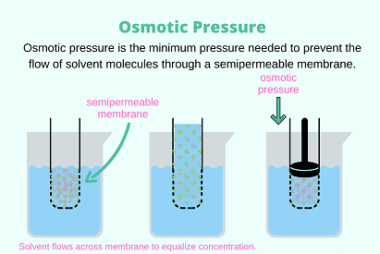
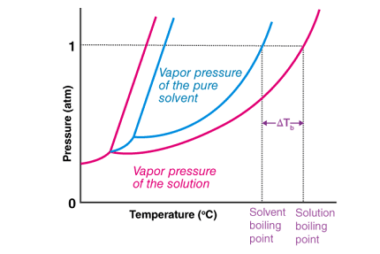
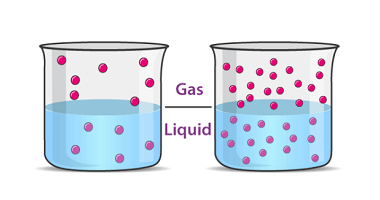
Electronic configuration of elements
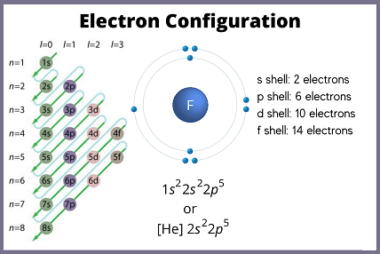
Here are the electronic configurations of the first 36 elements in the periodic table: What is Required Electronic configuration of elements The electronic configuration of an element refers to the arrangement of its electrons in the atomic orbitals of its atoms. This is usually represented using a notation that lists the occupied atomic orbitals and…