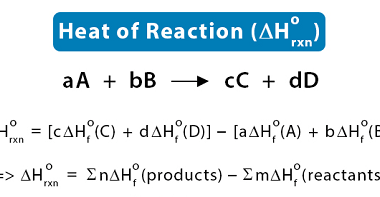Enthalpy of reaction
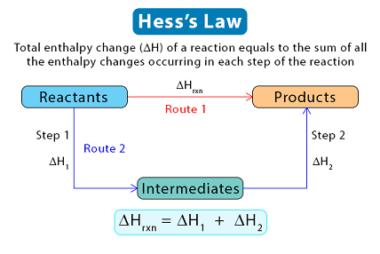
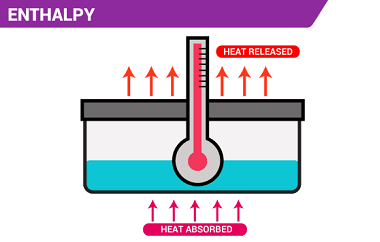
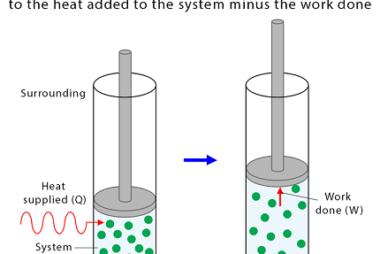
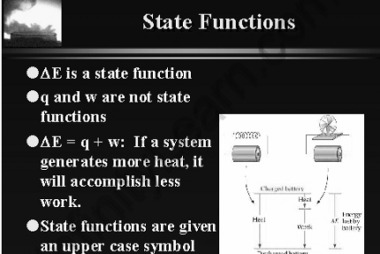
The enthalpy of reaction (ΔHrxn) is the amount of heat released or absorbed during a chemical reaction at a constant pressure. It represents the change in the enthalpy of the system as reactants are transformed into products. If the enthalpy of reaction is negative (ΔHrxn < 0), it means that the reaction is exothermic, and…