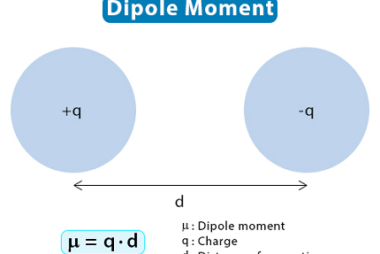
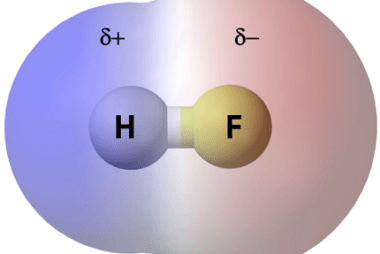
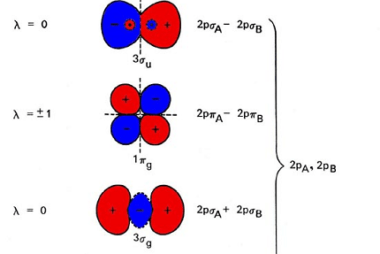
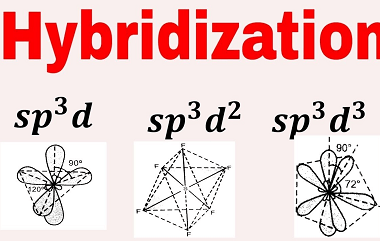
Triangular
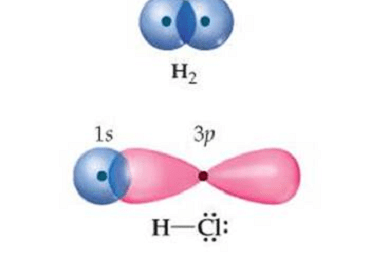
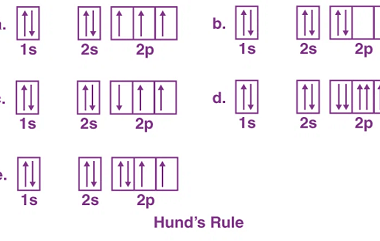
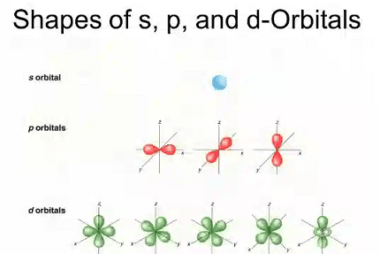
Triangular can refer to different things depending on the context. Here are a few possible interpretations: What is Required Triangular Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure In chemistry, triangular chemical bonding typically refers to a specific arrangement of atoms in a molecule where three atoms are bonded together in a triangular shape. This can occur in…