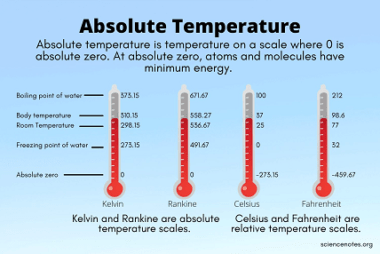
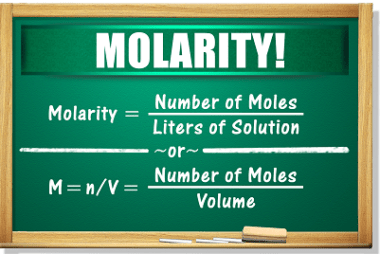
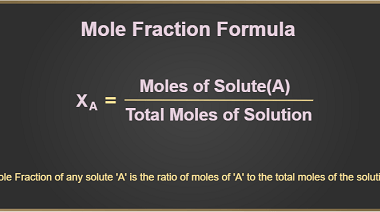
Root mean square and most probable velocities and their relation with temperature
Root mean square (RMS) velocity is a measure of the average speed of gas molecules in a sample at a given temperature. It is calculated as the square root of the average of the squares of the individual velocities of the molecules in the gas. Most probable velocity, on the other hand, is the speed…