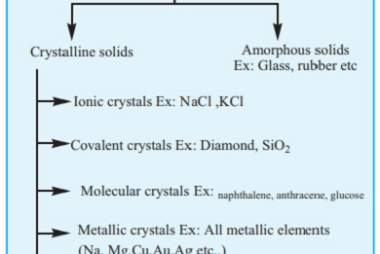
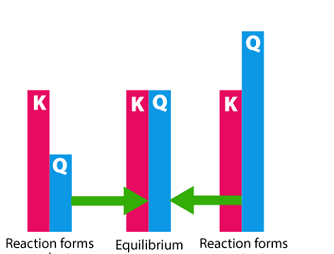
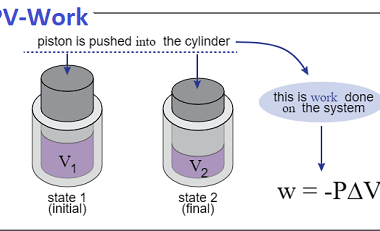
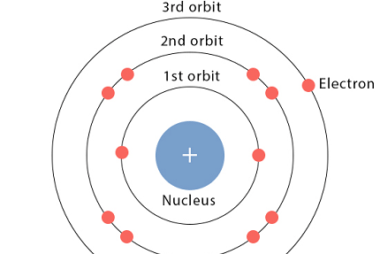
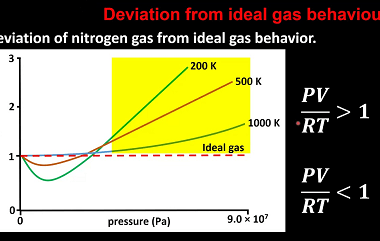
Crash Course AIIMS-SYLLABUS Chemistry syllabus Classification of solids based on different binding forces such as molecular
Classification of solids based on different binding forces such as molecular Please consult the specific syllabus or course materials provided by “Crash Course AIIMS-SYLLABUS Chemistry” for a comprehensive understanding of the topics covered in the chemistry section. What is Required AIIMS-SYLLABUS Chemistry syllabus Classification of solids based on different binding forces such as molecular The…