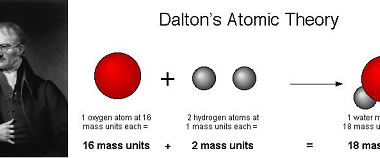
Gas laws and ideal gas equation
Gas laws describe the behavior of gases under different conditions, such as temperature, pressure, and volume. There are several gas laws, including Boyle’s law, Charles’s law, Gay-Lussac’s law, and the combined gas law, that relate these variables to one another. Boyle’s law states that at constant temperature, the volume of a gas is inversely proportional…