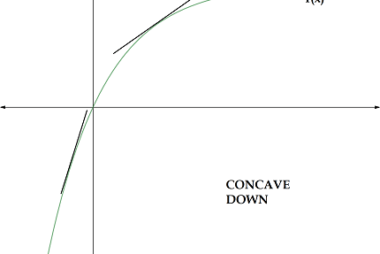
Derivatives of order two
The derivative of a function f(x) gives the rate of change of f(x) with respect to x. The derivative of order two, or the second derivative of f(x), represents the rate of change of the first derivative of f(x) with respect to x. Mathematically, the second derivative of f(x) is denoted as f”(x) or d^2/dx^2…