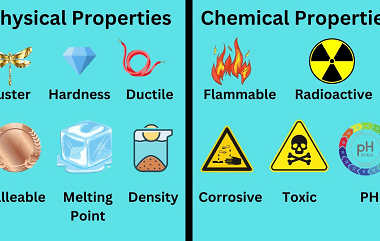
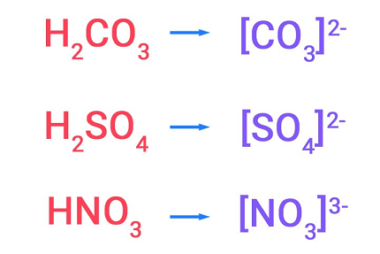
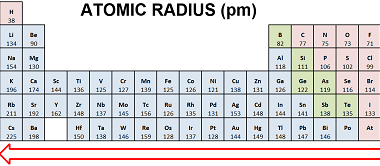
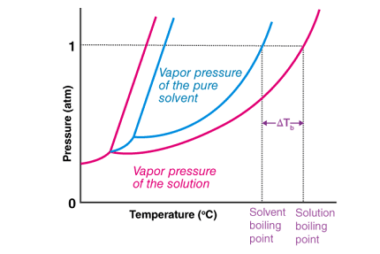
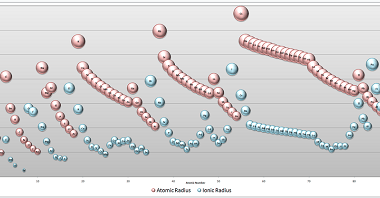
Properties
Properties refer to the characteristics or qualities of a thing or object that define its nature or identity. Some examples of properties include: What is Required Properties “Required properties” typically refers to properties that are essential or necessary for a particular object or system to function properly or fulfill its intended purpose. These properties may…