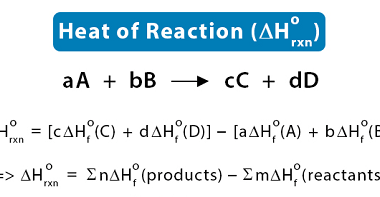Catalysis : Homogeneous and heterogeneous
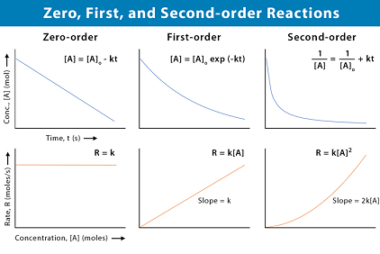
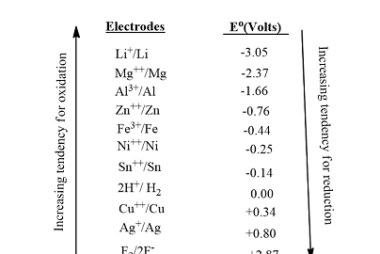
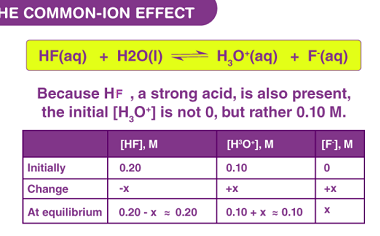
Catalysis refers to the process in which a catalyst increases the rate of a chemical reaction by providing an alternative pathway with lower activation energy. There are two types of catalysis: homogeneous catalysis and heterogeneous catalysis. Homogeneous catalysis involves a catalyst that is in the same phase (i.e., gas, liquid, or solid) as the reactants.…