Huygen’s principle
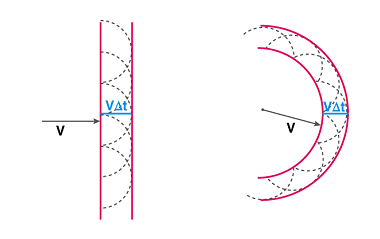
Huygen’s principle, named after the Dutch physicist Christiaan Huygens, is a fundamental principle in wave optics that explains how waves propagate through a medium. According to Huygen’s principle, each point on a wavefront can be considered as a source of secondary spherical waves. These secondary waves travel outwards from each point in all directions at…