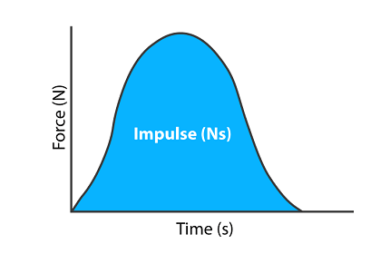
Terminal velocity
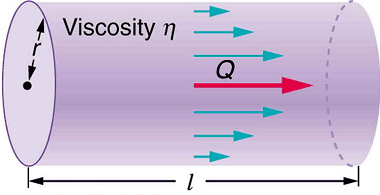
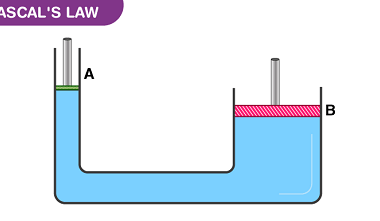
Terminal velocity is the maximum velocity that a falling object can reach when the resistance of the medium through which it is falling (such as air or water) balances the force of gravity. At terminal velocity, the object stops accelerating and falls at a constant speed. The terminal velocity of an object depends on its…