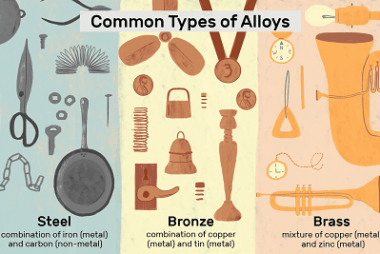
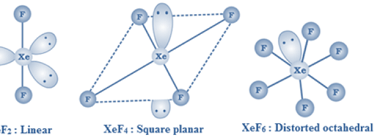
Linear
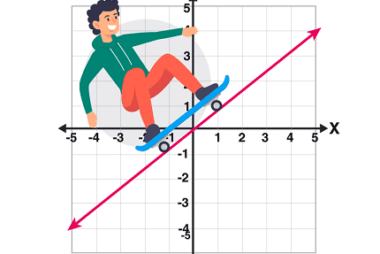
“Linear” refers to something that is arranged or operates in a straight line or a sequence of consecutive steps. In mathematics, linear typically refers to a function or equation that represents a straight line on a graph. For example, the equation y = mx + b is a linear equation, where “m” represents the slope…