Advance Course AIIMS-SYLLABUS Biology syllabus Sporulation
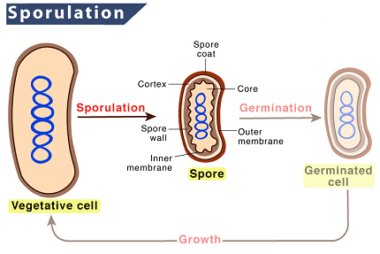
Sporulation Sporulation is a biological process observed in certain organisms, including bacteria, fungi, algae, and some protozoa. It is a form of reproduction or survival strategy that allows the organism to produce spores, which are specialized structures that can withstand harsh environmental conditions. In bacteria, sporulation occurs when the conditions for growth become unfavorable, such…