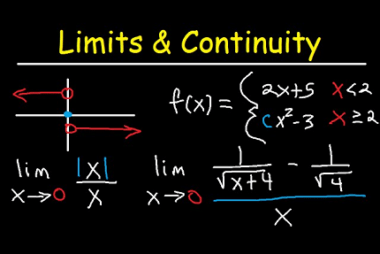
Close packed structure of solids (Cubic and Hexagonal)
Close-packed structures are arrangements of atoms or ions in a solid that result in the highest possible packing density. The two most common close-packed structures are the cubic close-packed (CCP) structure and the hexagonal close-packed (HCP) structure. In the CCP structure, also known as the face-centered cubic (FCC) structure, each atom or ion is surrounded…