Integrated Course AIIMS-SYLLABUS Physics syllabus Magnetic effects of Current and Magnetism
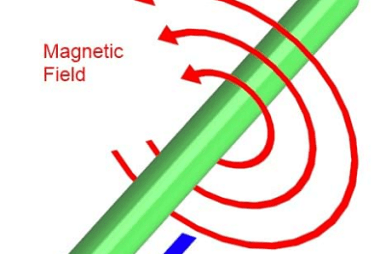
Magnetic effects of Current and Magnetism The study of magnetic effects of current and magnetism involves understanding the relationship between electricity and magnetism, specifically how electric currents produce magnetic fields and the interactions between magnetic fields and electric currents. Here are the key concepts covered in this topic: These are the fundamental concepts related to…