Standard electrode potentials
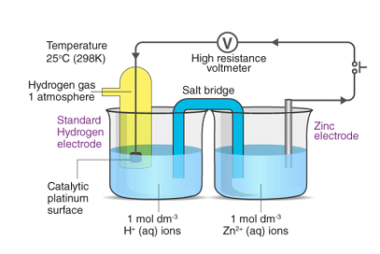
Standard electrode potentials (also known as standard reduction potentials) are a measure of the tendency of a chemical species to undergo reduction or oxidation under standard conditions. These potentials are reported relative to the standard hydrogen electrode (SHE), which is assigned a potential of 0.00 volts. Standard electrode potentials are typically represented using the notation…