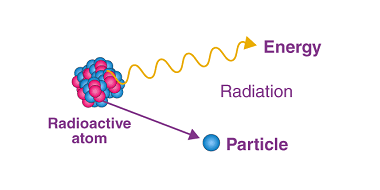
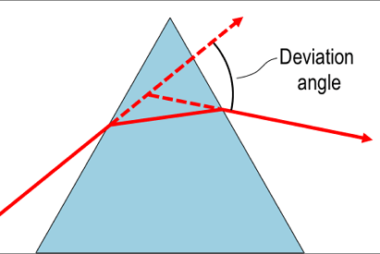
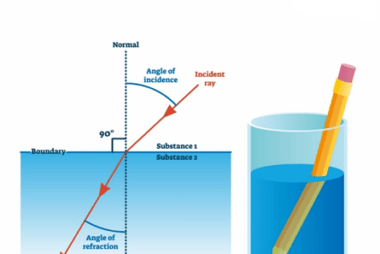
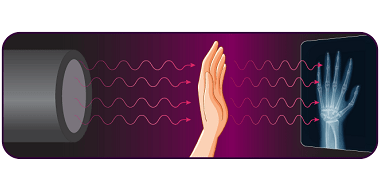
JEE (Main+Advance) e-advance Course Probability and Statistics
The JEE (Main+Advanced) e-advance course typically includes a section on probability and statistics. In this section, you can expect to learn about the following topics: To prepare for the probability and statistics section of the JEE (Main+Advanced) exam, you should start by familiarizing yourself with the basic concepts and principles of probability and statistics. You…