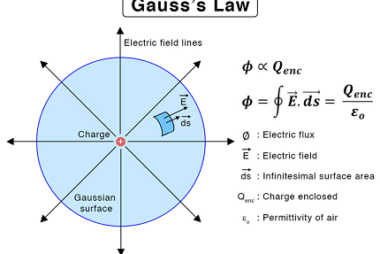
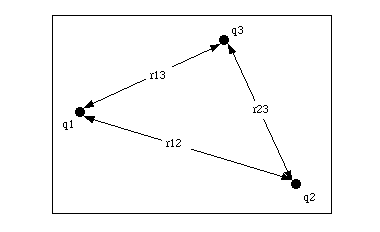
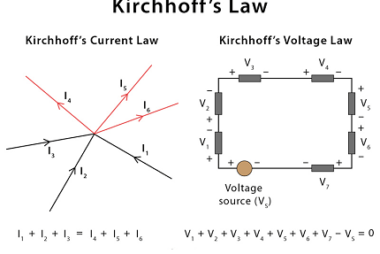
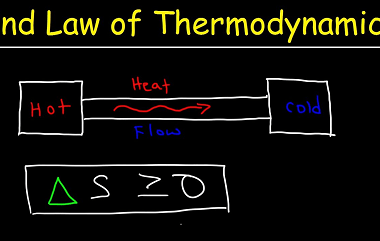
Cells
Cells are the basic unit of life and are the smallest structural and functional unit of living organisms. All living organisms, from the simplest unicellular organisms like bacteria to the most complex multicellular organisms like humans, are made up of cells. Cells have several components, including a cell membrane, cytoplasm, and genetic material. The cell…