Projectiles
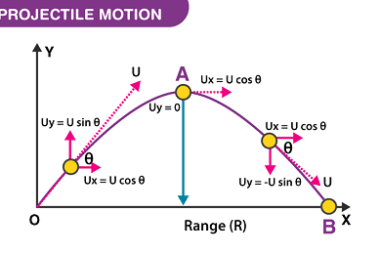
A projectile is any object that is thrown, shot, or launched into the air, and that moves along a ballistic trajectory. Projectiles are subject to the force of gravity, which causes them to follow a curved path known as a parabola. The motion of a projectile can be described by its initial velocity, angle of…