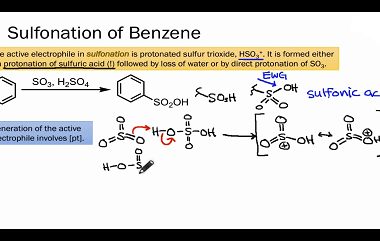
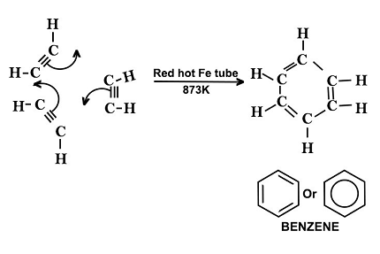
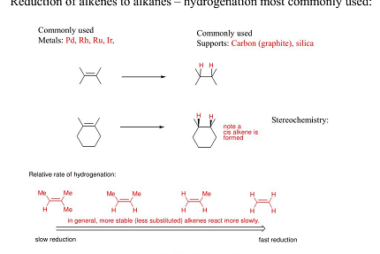
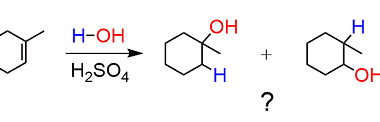
Sulphonation
Benzene sulphonation is a chemical reaction that involves the substitution of a hydrogen atom on the benzene ring with a sulfonic acid (-SO3H) group. This reaction is an important industrial process used to produce a variety of organic compounds, including detergents, dyes, and pharmaceuticals. The reaction typically involves treating benzene with concentrated sulfuric acid (H2SO4)…