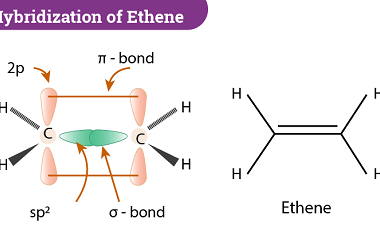
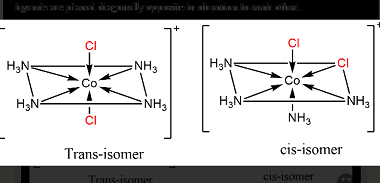
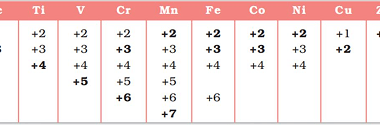
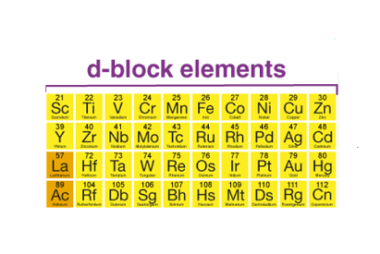
Hybridization and Geometries
Hybridization is a concept in chemistry that describes the mixing of atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals. Hybridization is important because it allows us to explain the geometry of molecules and the types of bonds that are present. The hybridization of an atom is determined by the number of electron groups around it, where…