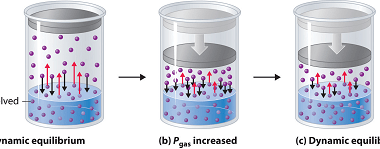
Integrated Course AIIMS-SYLLABUS Chemistry syllabus The solubility of the gas in liquids
The solubility of the gas in liquids The solubility of a gas in a liquid refers to the ability of the gas to dissolve in the liquid. It is a measure of the maximum amount of gas that can be dissolved in a given quantity of the liquid at a specific temperature and pressure. The…