Integrated Course AIIMS-SYLLABUS Chemistry syllabus Colloid Properties
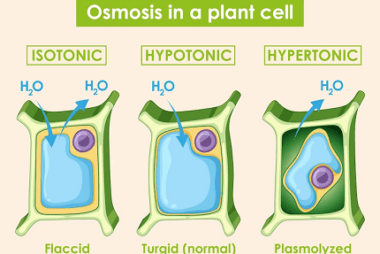
Colloid Properties Colloid properties refer to the characteristics and behaviors of colloidal systems, which are heterogeneous mixtures consisting of two or more phases. The dispersed phase is composed of particles or droplets, while the dispersion medium is the continuous phase in which the particles are dispersed. Here are some important colloid properties: These are some…