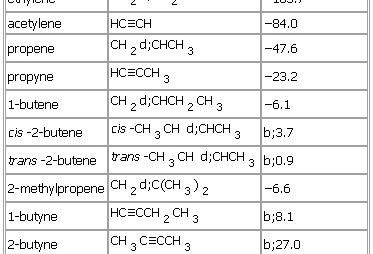
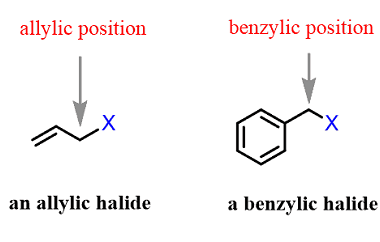
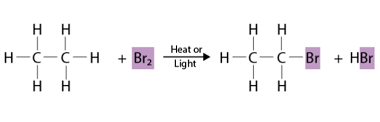
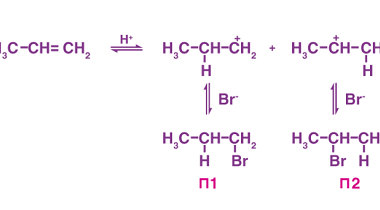
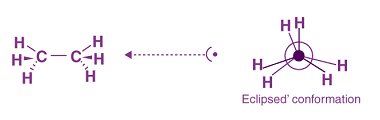
Preparation by elimination reactions
Elimination reactions are a type of organic reaction where a molecule loses one or more atoms or groups of atoms to form a double bond or a triple bond. The most common type of elimination reaction is called a beta-elimination, where the atom or group of atoms that is eliminated is adjacent to a leaving…