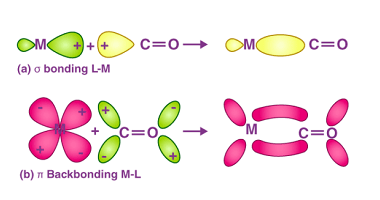
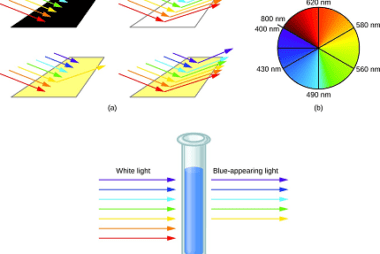
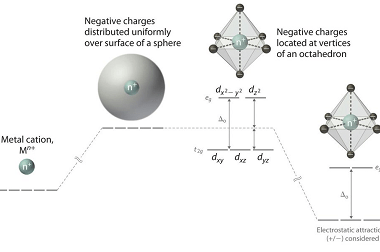
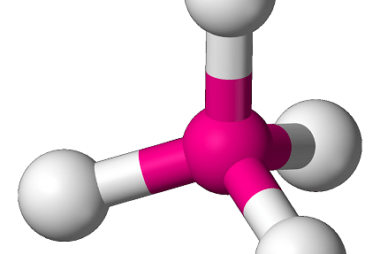
Nitrate
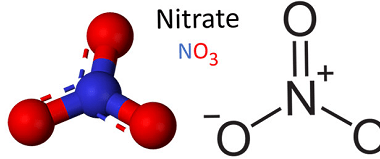
Nitrate is a chemical compound that consists of one nitrogen atom and three oxygen atoms, with a chemical formula of NO3-. It is an anion, meaning it carries a negative charge, and is commonly found in the environment as a result of natural processes such as the nitrogen cycle and lightning strikes, as well as…