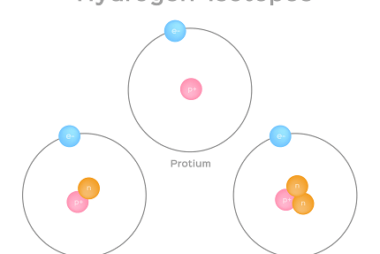
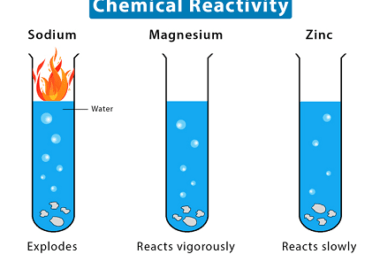
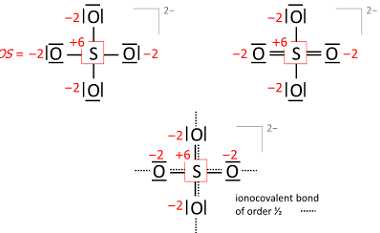
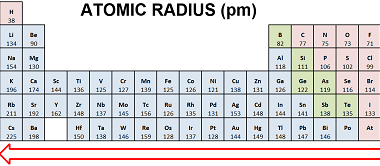
Hydrides – Ionic, Covalent and Interstitial
Hydrides are compounds that contain hydrogen and one or more other elements. They can be classified into three main types: ionic hydrides, covalent hydrides, and interstitial hydrides. Ionic hydrides are formed by the reaction of hydrogen with metals, such as alkali metals (group 1), alkaline earth metals (group 2), and some transition metals. These hydrides…