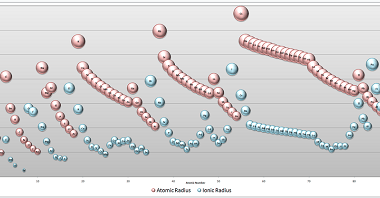
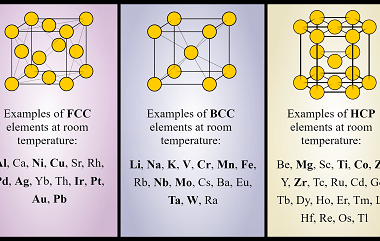
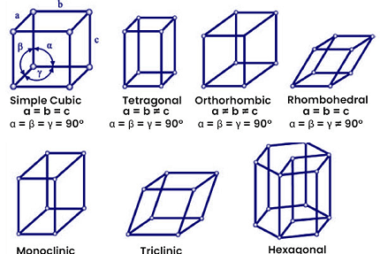
Modern periodic law and the present form of periodic table
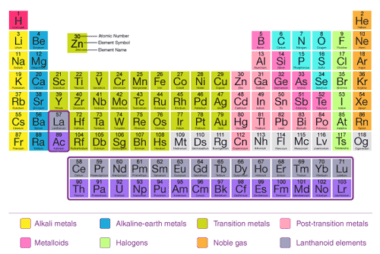
The modern periodic law states that the properties of elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers. This means that when elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physical properties. The present form of the periodic table is based on the modern periodic law…