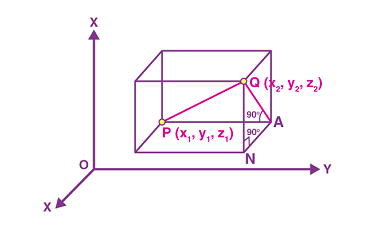
Three dimensions: Distance between two points
The distance between two points in three-dimensional space can be found using the following formula: d = √((x2 – x1)^2 + (y2 – y1)^2 + (z2 – z1)^2) where (x1, y1, z1) and (x2, y2, z2) are the coordinates of the two points, and d is the distance between them. To use the formula, you…