Standard electrode potentials
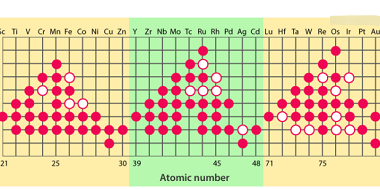
Here are the standard electrode potentials of some d-block elements: Element Standard electrode potential (V) Scandium (Sc) -2.58 Titanium (Ti) -1.63 Vanadium (V) -1.18 Chromium (Cr) -0.91 Manganese (Mn) -1.18 to -1.57 (depending on oxidation state) Iron (Fe) -0.44 to -0.77 (depending on oxidation state) Cobalt (Co) -0.28 Nickel (Ni) -0.25 Copper (Cu) +0.34 Zinc…