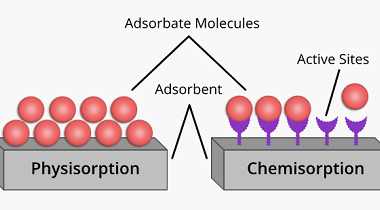
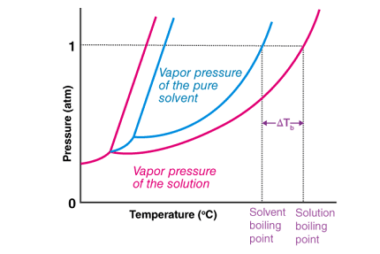
Ionic radius
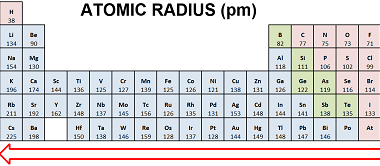
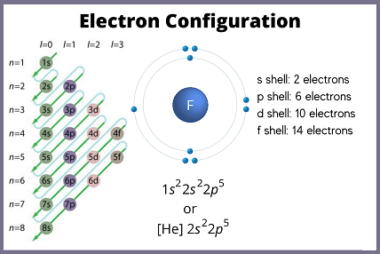
Ionic radius refers to the size of an ion, which is an atom or a group of atoms that has gained or lost one or more electrons, resulting in a net positive or negative charge, respectively. The ionic radius is defined as half the distance between the nuclei of two ions that are just touching…